As the coding landscape continues to evolve, the question of whether to embrace ReactJS becomes increasingly pertinent for developers seeking to enhance their skill set. Known for its modular components and dynamic capabilities, ReactJS presents a compelling proposition, but the decision to delve into this JavaScript library requires careful consideration. We tackle the fundamental questions surrounding the adoption of ReactJS. By exploring its impact on skill acquisition and career growth, we aim to assist readers in making a discerning choice about the relevance of ReactJS in their coding journey.
1. Is learning ReactJS hard?
Learning ReactJS can be challenging for beginners, especially for those who are new to JavaScript and front-end development. ReactJS, a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces, particularly single-page applications, is known for its efficiency and flexibility.
However, the learning curve can vary depending on your background:
- For Complete Beginners: It might be more challenging if you start without any prior JavaScript experience. React builds upon JavaScript, so understanding the basics of JavaScript, HTML, and CSS is crucial before diving into React.
- For Experienced Developers: Learning React will be easier if you already have a solid foundation in JavaScript and understand concepts like DOM manipulation and ES6 features. You’ll need to adapt to React’s component-based architecture and learn its unique features like JSX (a syntax extension), state management, and the component lifecycle.
- Availability of Resources: React has a strong community and a wealth of learning resources available, including official documentation, tutorials, online courses, and community forums. This abundance of resources makes it easier for learners to find answers and guidance.
Hands-On Practice: Like any other programming skill, the key to mastering React is practice. Building small projects and incrementally increasing the complexity as you learn more about React’s features and best practices can significantly ease the learning process.
2. Is it worth learning React in 2024?
Yes, learning React in 2024 is worth it for anyone interested in web development.
Learning React remains a valuable investment for several reasons:
- Industry Demand: React continues to be one of the most popular front-end libraries, widely used in the industry. Many companies, from startups to large enterprises, use React in their tech stack, creating a steady demand for React developers.
- Community and Ecosystem: React has a strong community and a rich ecosystem. This means extensive resources for learning, a vast array of libraries and tools, and regular updates and improvements to the library itself.
- Career Opportunities: Proficiency in React opens up numerous job opportunities in web development. The skills acquired are not just limited to React itself but are transferable to other areas of JavaScript development.
- Versatility and Performance: React’s component-based architecture allows for building reusable UI components, making it a versatile choice for various applications, from small-scale projects to large, complex web applications.
- Complementary Technologies: Learning React also aligns well with other popular technologies in web development, such as Node.js for the backend and React Native for mobile app development, enhancing your skill set even further.
3. Is learning React enough to get a job?
Learning React can significantly enhance your job prospects in web development, but it may not be enough on its own. Employers often look for a broader set of skills:
- JavaScript Proficiency: A strong understanding of JavaScript is essential, as React is a JavaScript library.
- Additional Technologies: Familiarity with HTML, CSS, and other JavaScript libraries or frameworks can be beneficial.
- Backend Skills: Basic knowledge of a backend language or framework complements front-end skills well.
- Soft Skills: Problem-solving skills, adaptability, and teamwork are also crucial in a work environment.
While React is valuable, a well-rounded profile with a mix of technical and soft skills is typically more appealing to employers.
4. Should I learn Next.js or React first?
When deciding whether to learn Next.js or React first, it’s generally advisable to start with React. React is a fundamental library for building user interfaces, and understanding it is crucial before diving into Next.js, which is a framework built on top of React.
By learning React first, you gain a solid foundation in the concepts and patterns that Next.js builds upon, making it easier to grasp the additional features and optimizations that Next.js offers, such as server-side rendering and static site generation. Once comfortable with React, moving on to Next.js will be a natural progression in your learning journey.
5. How long does it take to learn ReactJS?
The time it takes to learn React fully varies depending on your existing knowledge and experience in web development, particularly JavaScript. Generally, it takes 3-6 weeks to get comfortable with the basics and 3-6 months to gain proficiency in more complex aspects. Regular practice and building projects are key to solidifying your understanding and skills in React.
6. Can I master React in 3 months?
Mastering React in 3 months is ambitious but possible, especially with dedicated study and practice. Your progress will depend on your prior experience with JavaScript and web development and the time you can commit daily. Immersive learning, building projects, and consistent practice are important for deepening your understanding and proficiency in React within such a timeframe. However, mastery also involves understanding best practices, which develop over time and experience.
7. Is React hard to learn if you know Angular?
If you’re already familiar with Angular, learning React might be easier for you. Both are popular JavaScript frameworks with their own unique principles, but having experience in Angular means you’re already adapted to concepts like components, directives, and dependency injection, which are somewhat analogous to patterns in React. The main challenge might be adapting to React’s JSX syntax and understanding its unidirectional data flow. Overall, your Angular experience will be beneficial as you transition to React.
8. Is React harder to learn than Vue?
Whether React is harder to learn than Vue largely depends on your background and personal preference. React has a steeper learning curve due to its JSX syntax and more complex state management. Vue, on the other hand, is often considered more straightforward and easier to integrate into existing projects. However, React’s concepts might not be as challenging for those already familiar with JavaScript frameworks. Ultimately, both have their intricacies, and the ease of learning can vary from person to person.
9. Should I start with Vue or React?
Choosing between starting with Vue or React depends on your preferences and goals. Vue is a great choice if you prefer a gentle learning curve and straightforward documentation. It’s known for being intuitive and easy to integrate. On the other hand, if you’re aiming for broader industry applicability and are interested in a more extensive ecosystem, React might be the better option. React’s community and job market presence are significant advantages for those looking to build a career in web development.
ReactJS Career and Job Market Outlook for 2024
1. Are React Developers well paid?
Yes, React developers are generally well-compensated. The demand for React skills in the job market is high, as it’s one of the most popular frameworks for web development. This demand often translates to competitive salaries, especially for developers skilled in React and other complementary technologies and modern web development practices. The exact salary can vary based on factors like location, experience, and the complexity of the projects involved.
2. What is the average React JS salary?
The average salary for a React JS developer varies widely depending on factors such as location, experience, and the specific demands of the job market. According to Glassdoor, in the United States, the average salary can range from $83K to $137K per year for experienced developers. In other regions, these figures can differ significantly. It’s important to consider local industry standards and cost of living when evaluating salary expectations.
3. Why are React developers paid so much?
React developers are often well-compensated due to a combination of high demand for their skills and the value they bring to businesses. React’s popularity in building dynamic, efficient web applications means that developers proficient in it are in demand. Additionally, their expertise in creating user-friendly interfaces directly contributes to the success of web projects, often translating to better user engagement and business outcomes. This combination of high demand and significant impact on project success makes their skills valuable in the job market.
4. Is React getting less popular?
As of 2024, React is not losing popularity but rather maintaining a strong position in the web development community. Its widespread adoption by developers and companies and the continuous updates and improvements to the library have kept it relevant and popular. However, the tech landscape is dynamic, and new frameworks or trends might emerge. Keeping an eye on industry trends is always a good idea to stay current.
React’s position as of late 2023 indicated a continuing strong presence in the industry (Source: Statista). Nonetheless, it’s always beneficial for developers to stay informed about emerging technologies and shifts in the tech landscape.
5. What is the hourly rate for React developers?
The hourly rate for React developers can vary widely based on several factors, such as geographical location, level of experience, and the project’s complexity. According to GlassDoor, in the United States, hourly rates can range from $37 to $57 for highly experienced developers. In other countries, rates can differ significantly due to local economic conditions and demand for React skills. Freelance React developers may also have varying rates compared to those working in a company. For the most current and region-specific information, consulting local job markets or freelance platforms can provide a clearer picture of the current rates.
6. Is there a shortage of React developers?
As of 2024, there is a high demand for React developers, which sometimes outpaced the supply, creating a perception of shortage in some markets. This demand is driven by the widespread adoption of React for web development across various industries.
However, the actual shortage can vary by region and time, influenced by factors like the rapid growth of the tech industry, the appeal of React as a skill in the developer community, and the rate at which new developers are trained in React. This dynamic means that while there may be high demand in certain areas or at certain times, the global tech community is continually adapting to meet these needs.
7. What is the salary of a React developer for 1 year of experience?
The salary of a React developer with one year of experience varies depending on location, the type of company, and the specific demands of the role. According to Coursera, the salary for a junior React developer with 1 year of experience in the United States ranges from $78K to $88K per year. This figure can differ in other regions, often aligning with the local cost of living and the overall demand for tech talent.
Prerequisites and Prior Knowledge
Can I start React without knowing JavaScript?
Starting React without a basic understanding of JavaScript is not recommended. React is a JavaScript library, so knowing JavaScript is essential for understanding how React works and for effectively using it to build web applications. A solid foundation in JavaScript, including familiarity with concepts like variables, functions, arrays, objects, and ES6 features, will significantly ease the learning process in React. Getting comfortable with JavaScript basics is advisable before diving into React.
Technology Framework Comparisons and Choices
1. Should I learn Angular or React?
Choosing between learning Angular or React depends on your specific needs, career goals, and preferences:
- Project Scope: If you’re interested in building large-scale, enterprise-level applications, Angular might be more suitable due to its comprehensive framework, which includes built-in solutions for routing, state management, and form validation.
- Learning Curve: React has a gentler learning curve and is often considered more approachable. It’s versatile for various project sizes, and you can integrate it gradually into your projects.
- Community and Job Market: React generally has a larger community and wider job market presence. This can translate to more learning resources and job opportunities.
Personal Preference: Some developers prefer Angular’s structured and comprehensive nature, while others enjoy React’s flexibility and the freedom it offers in choosing additional libraries and tools.
2. Should I learn Angular or React in 2024?
Choosing between learning Angular or React in 2024 depends on your career goals, project requirements, and personal learning style:
- Career Goals: React tends to have a broader market appeal for web development roles. If your goal is versatility in job opportunities, React might be more beneficial.
- Project Type: Angular’s comprehensive framework is often preferred for large-scale, enterprise-level applications. With its component-based architecture, React is well-suited for scalable, dynamic web applications.
- Learning Curve: React is generally considered to have a gentler learning curve and offers more flexibility in terms of integrating with other libraries.
Community and Ecosystem: Both have strong communities and ecosystems, but React’s is larger, which might translate to more resources and community support.
3. Should I learn Flutter or React in 2024?
Choosing between learning Flutter or React in 2024 depends on your specific goals and interests:
- Web vs. Mobile Development: React is primarily used for web development, especially for building dynamic user interfaces. Flutter, on the other hand, is a framework for building cross-platform mobile applications (iOS and Android).
- Career Opportunities: React’s widespread use in web development offers many job opportunities. Flutter is gaining traction in mobile app development, but its market presence is smaller compared to React in the web domain.
- Learning and Community Support: React has a large community and a wealth of learning resources. Flutter, supported by Google, is also growing its community and resource base.
- Personal Interest and Project Requirements: If you’re more interested in web development, React is a great choice. If you’re leaning towards mobile app development, especially cross-platform, Flutter is the way to go.
Your decision should align with the type of development you’re most interested in and the skills that are most relevant to your career path or project needs.
4. Is React or Angular more in demand?
As of 2024, React has a higher demand in the job market compared to Angular. This trend was reflected in the number of job listings requiring React skills and the broader adoption of React by companies for their web development projects. However, Angular also maintained a significant presence, particularly in enterprise-level applications and among companies that prefer a full-framework approach.
It’s important to note that demand can vary based on the specific industry, region, and the type of projects companies are undertaking. React’s popularity is often attributed to its flexibility, ease of learning, and large community support, while Angular is favored for its robustness and suitability for large-scale applications. Keeping an eye on current job market trends and industry needs in your specific area will give the most accurate picture of demand.
5. Does Angular pay more than React?
The salary for developers skilled in Angular versus React doesn’t have a clear-cut difference solely based on the framework.
Instead, it often depends on various factors:
- Job Role and Experience: Salaries can vary based on the specific role (e.g., front-end, full-stack) and the individual’s experience level.
- Location: Geographic location significantly influences salary ranges due to the cost of living and local demand for tech skills.
- Company Size and Industry: Larger companies or those in certain industries might offer higher salaries, irrespective of the specific technology.
- Project Complexity: More complex projects requiring advanced skills in either framework might command higher pay.
Overall, both Angular and React skills can lead to well-compensated positions in the tech industry. The choice between the two should also consider personal interest, project needs, and long-term career goals.
6. Why is Angular harder than React?
Angular is often perceived as harder than React due to its comprehensive nature. Angular is a full-fledged framework offering a wide array of built-in functionalities like dependency injection, routing, and form handling, which requires a broader understanding upfront.
In contrast, React, a library focused on UI components, allows developers to integrate only the needed parts and will enable them to choose additional libraries as required. This focused and modular approach can make React seem more approachable, especially for beginners. Angular’s learning curve is steeper, but it provides a more structured environment, which can benefit large-scale applications.
7. What companies use Angular vs React?
Companies choose Angular or React based on their project requirements and architectural preferences:
Angular
This full-fledged framework is often chosen by enterprises for its robustness and comprehensive features.
Companies using Angular include:
- Microsoft Office
- Deutsche Bank
- Mixer
- Santander
- Gmail
- Forbes
- UpWork
- PayPal
- Grasshopper
- Samsung
- Delta
- Overleaf
React
Its flexibility and component-based architecture make it popular for various applications. Facebook (Meta), which created React, uses it extensively, as do other companies like Airbnb, Netflix, and Instagram.
Companies using React include:
- Facebook (Meta): Not only created React but also uses it extensively across its products, including Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp.
- Airbnb: Leverages React for its user-friendly accommodation booking platform.
- Netflix: Netflix Uses React for its web interface to provide a seamless streaming experience.
- Instagram: Heavily relies on React for its web application.
- Uber: Utilizes React in its web applications for both riders and drivers.
Various companies across different industries use both Angular and React, and the choice often depends on the specific needs of the project and the company’s existing technology stack.
8. Is Netflix made by React or Angular?
Netflix primarily uses React for its front-end development. They have adopted React due to its efficient performance and its ability to handle dynamic user interfaces effectively. The choice of React aligns with Netflix’s need for a scalable, fast, and responsive user interface to deliver a seamless streaming experience to millions of users worldwide. While also popular for many applications, Angular is not the primary framework that Netflix uses for its front-end architecture.
9. Why do people choose Angular over React?
People choose Angular over React for several reasons:
- Full Framework: Angular is a complete framework offering built-in solutions for common development needs like routing, forms handling, and dependency injection, which can streamline the development process.
- TypeScript Integration: Angular is built with TypeScript, which provides strong typing and object-oriented programming features, making it appealing for developers who prefer these aspects for larger, more complex projects.
- Structured Approach: Angular’s opinionated nature enforces a specific way to organize code, which can lead to more consistent and maintainable codebases, especially in large teams or projects.
- Enterprise Use: Angular’s comprehensive features and robustness make it a popular choice for enterprise-level applications where the full-framework approach is beneficial.
Ultimately, the choice between Angular and React often comes down to the project’s specific requirements and the development team’s preferences.
10. Should I switch from React to Angular?
Whether you should switch from React to Angular depends on several factors:
- Project Requirements: Switching might be beneficial if your upcoming projects or the company you are working with prefers Angular for its comprehensive features and full-framework capabilities.
- Learning and Career Goals: If you aim to diversify your skillset or your career path benefits from having expertise in both, learning Angular can be a valuable addition.
- Team Environment: If your team or organization is transitioning to Angular, aligning with their technology stack could benefit collaboration.
- Personal Preference: Some developers prefer Angular’s structured framework and TypeScript integration. A switch might be productive for you if these align with your development style.
It’s important to weigh these factors against the need to stay updated with React, especially if it remains widely used in your current or desired job market. Both frameworks have their strengths and are valuable in the job market.
11. Do React and Angular work together?
No, React and Angular are typically not used in the same project because they are designed to manage the view layer of web applications and have different philosophies and architectures. Using them together would complicate the project without providing clear benefits. Generally, developers choose one based on project requirements, team expertise, and the specific characteristics of each framework or library.
With its component-based approach, React is often selected for its flexibility and simplicity, while Angular is chosen for its comprehensive nature and robust features for larger, more complex applications. Mixing them would negate these individual strengths and likely lead to issues in maintainability and scalability.
12. Is React more flexible than Angular?
Yes, React is more flexible than Angular. This flexibility stems from React being a library focused on building user interfaces, primarily through its component-based architecture. It allows developers to choose other libraries and tools as needed for things like state management and routing, offering a more customizable approach to building applications. In contrast, Angular is a full-fledged framework that provides a more rigid structure with built-in functionalities for various aspects of development. This comprehensive nature of Angular can benefit certain projects but might not offer the same level of flexibility as React in integrating different tools and libraries.
13. Why choose React over Angular?
Choosing React over Angular is advisable in several scenarios:
- Simpler Learning Curve: If you or your team require a quicker ramp-up time, React, with its more straightforward approach and smaller API surface, can be easier to start with.
- Flexible Architecture: For projects where you prefer to have the freedom to select different libraries and tools for various needs like routing and state management, React’s unopinionated nature is beneficial.
- Dynamic Web Applications: React’s efficient rendering and component-based architecture make it ideal for projects that require highly dynamic and interactive user interfaces.
- Large Community and Ecosystem: If you value a large community for support and a wide range of available resources, React’s popularity ensures an abundance of learning materials and third-party libraries.
- Project Scale and Complexity: For smaller to medium-scale projects, or when you need to update or scale an existing application incrementally, React’s modular nature can be particularly advantageous.
The decision should align with the project’s specific requirements, the team’s expertise, and the desired flexibility and scalability of the application.
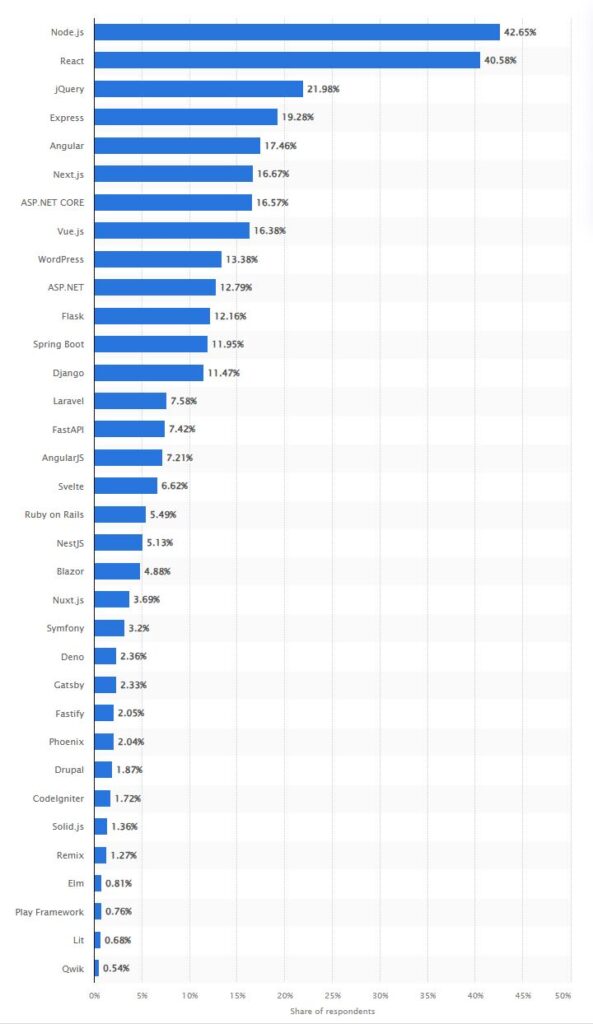
14. How popular is React vs Angular vs Vue?
React, Angular, and Vue each have their own popularity and use cases in the web development community:
1. React
React is often considered the most popular among the three. Its large community, backed by Facebook, extensive libraries, and the ease of learning and using React contribute to its widespread adoption. It’s particularly popular for building dynamic, high-performing web and mobile applications.
2. Angular
Angular, maintained by Google, is a comprehensive framework used especially in enterprise-level and large-scale applications. Its popularity is significant, though generally, it’s seen as less widespread than React. Angular’s robustness and full-fledged features make it a preferred choice for more complex applications.
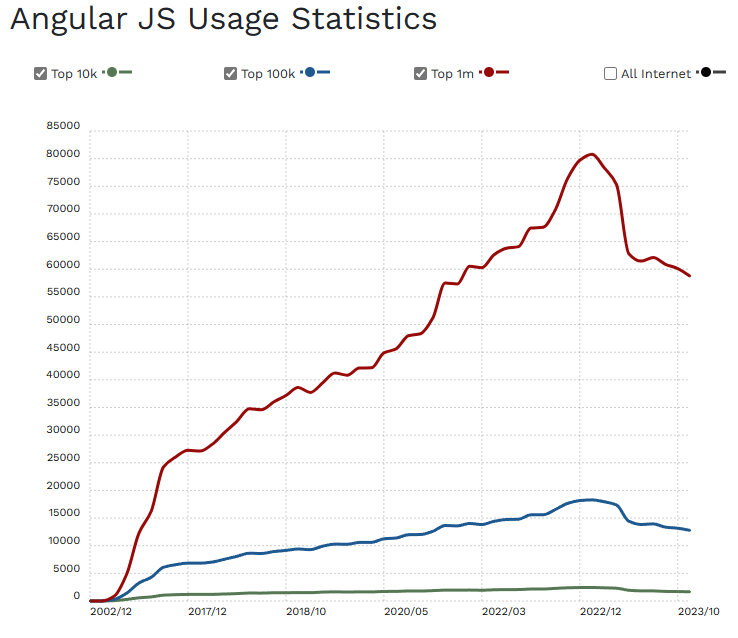
3. Vue
Vue, while smaller in community size compared to React and Angular, has been growing steadily in popularity. It’s appreciated for its simplicity, detailed documentation, and ease of integration. Vue is often chosen for its gentle learning curve and is popular among small to medium-sized projects.
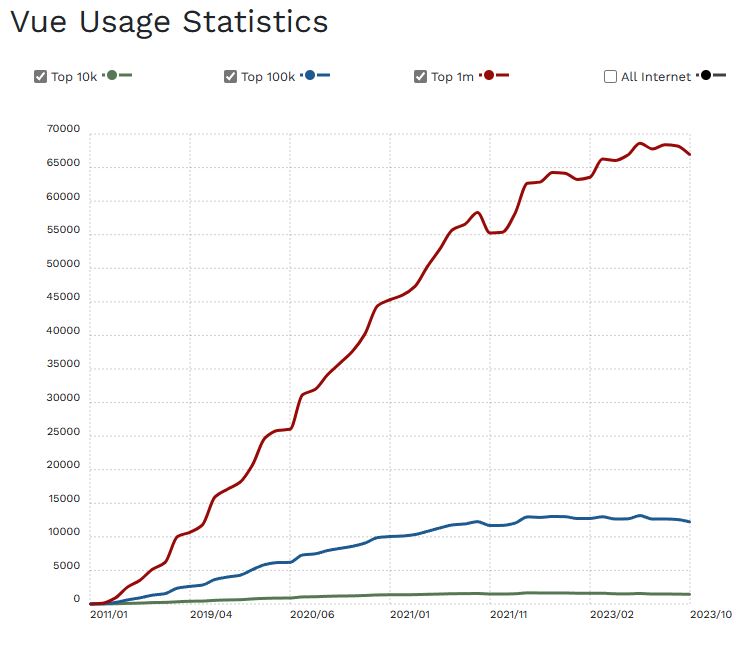
As of 2023, React lead in popularity and usage, followed by Angular and Vue, but the best choice depends on project requirements, team skills, and the application’s specific needs. Each has its strengths and caters to different aspects of web development. Though these stats are likely to change into 2024, it’s unlikely that React will drop in popularity in any meaningful way.
15. Why people prefer Vue over React?
People might prefer Vue over React for several reasons:
- Simplicity and Ease of Learning: Vue is often considered more straightforward and easier to pick up than React, especially for those new to JavaScript frameworks. Its clear and comprehensive documentation aids in this.
- Detailed Documentation: Vue’s documentation is highly praised for being thorough and user-friendly, which can be a significant advantage for beginners when troubleshooting or learning new concepts.
- Integration Flexibility: Vue is simpler to integrate into existing projects, as it can be adopted incrementally. This is particularly beneficial for projects that need a gradual transition.
- Reactive Data Binding: Vue’s handling of reactive data binding is straightforward and requires less boilerplate code compared to React, making state management simpler in many cases.
- Template Syntax: Vue’s HTML-based template syntax is familiar and easy to understand for those with a background in HTML and CSS, whereas React’s JSX might present a steeper learning curve.
- Community and Ecosystem: While Vue’s community is smaller than React’s, it is very active and supportive, which can be appealing for developers seeking a more tightly-knit community.
These reasons make Vue an attractive choice, particularly for smaller projects or developers and teams looking for a balance between functionality and ease of use.
16. Why people use Vue instead of React?
People may choose Vue over React for several reasons:
- Ease of Integration: Vue is known for its ease of integration into existing projects, making it a good choice for enhancing the front-ends of existing applications without a complete overhaul.
- Simplified Syntax and Learning Curve: Vue’s template syntax is straightforward, especially for those with a basic understanding of HTML and CSS. This simplicity can make the learning curve less steep compared to React’s JSX.
- Reactivity and Two-Way Data Binding: Vue’s reactivity system and built-in two-way data binding (v-model) simplify certain tasks, reducing the need for additional state management libraries.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Vue is often praised for its well-written and detailed documentation, making it easier for new developers to get started and find resources.
- Flexibility and Modularity: Vue offers a balance of flexibility and structure, providing a guided approach without being too opinionated. This appeals to developers who seek a middle ground between React and Angular.
- Community and Ecosystem: While smaller than React’s, Vue’s community is vibrant and supportive, and the ecosystem around Vue has been growing steadily.
These factors make Vue a compelling option for developers and teams looking for a progressive framework that is both powerful and approachable.
17. Should I learn Vue or React in 2024?
Deciding whether to learn Vue or React in 2024 depends on your goals and preferences. If you value a framework with a straightforward learning curve and a more traditional approach to web development, Vue might be the right choice. It’s known for its ease of understanding, especially for those with basic HTML, CSS, and JavaScript knowledge.
On the other hand, if you’re looking for a skill with a broad range of applications and high demand in the job market, React could be more suitable. React’s component-based approach offers flexibility in developing various web applications and is widely used in the industry. Both have strong communities and are continuously evolving, so consider what aligns best with your career objectives and the type of projects you want to work on.
18. Is Angular still in demand?
Yes, as of 2023, Angular was still in demand, particularly in enterprise-level and large-scale application development. Angular’s comprehensive framework, which includes a wide range of built-in functionalities like routing, forms handling, and dependency injection, makes it a preferred choice for many large companies and complex projects. Its robustness, scalability, and maintenance support by Google contribute to its ongoing popularity in certain industry sectors. While web development trends can shift, Angular’s role in creating structured, efficient, scalable applications keeps it relevant in the job market.
19. Does Netflix use Vue or React?
Netflix primarily uses React for its main front-end development, particularly for its streaming service. React’s efficiency in handling dynamic user interfaces suits their need for a scalable and responsive main user interface.
While Vue is another popular front-end framework, Netflix has utilized Vue.js in some smaller internal applications, demonstrating the company’s openness to employing different technologies based on specific project needs.
20. Why is Vue not as popular?
Vue, while increasingly popular, may not have the same level of widespread adoption as React or Angular for a few reasons:
- Vue emerged later than React and Angular, which had already established strong positions in the market.
- React’s backing by Facebook and Angular’s by Google gave them a visibility and perceived credibility boost that Vue, as an independently developed framework, doesn’t have.
- Vue’s popularity initially grew more rapidly in China and East Asia, which may have contributed to a perception of it being less dominant in the Western tech market.
Despite these factors, Vue’s community is growing, and it’s recognized for its ease of use and flexibility, making it a popular choice for many developers and projects worldwide.
Technical Aspects and Trends
1. Are React classes obsolete?
React Classes are not obsolete, but the introduction and growing popularity of React Hooks since their release in React 16.8 have shifted the trend toward functional components. Hooks allow for using state and other React features in functional components, which were previously only possible in class components. This shift is driven by the simplicity and cleaner code that functional components with Hooks offer.
However, class components are still a valid and functional part of React, and many existing applications use them. The React community and documentation often recommend using functional components and Hooks for new projects, but understanding class components remains valuable, especially for maintaining and updating legacy projects.
2. Is React a front-end or back-end?
React is a front-end library. It’s used primarily for building user interfaces, particularly for web applications. React allows developers to create reusable UI components, manage the state of these components, and render them efficiently in the browser.
While React handles the view layer in the front-end, it can be integrated with various back-end technologies for full-stack development. React does not provide back-end capabilities itself; for server-side logic, databases, and other back-end functionalities, other technologies are used in conjunction with React.
3. Can I use TypeScript with React?
Yes, you can use TypeScript with React. TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript, offers additional features like static typing, which can enhance the development experience, particularly in larger applications or when working in teams. It helps in catching errors early in the development process, improving code quality and maintainability. React and TypeScript work well together, and the React ecosystem, including tools and libraries, generally supports TypeScript. Using TypeScript with React can lead to more robust and error-resistant code, making it a popular choice for many developers.
Industry and Real-World Applications
1. Is Facebook dropping React?
As of 2024, there is no indication that Facebook (now Meta Platforms, Inc.) is dropping React. React was developed and is maintained by Facebook and continues to be a core part of their technology stack. Facebook uses React extensively in its products and continues to invest in its development and enhancement. React’s popularity and active development, both within Facebook and in the broader developer community, suggest that it remains an integral and supported technology for Facebook.
2. Is Facebook built using React?
Yes, Facebook is built using React. React was originally developed by Facebook engineers and is extensively used in Facebook’s web application. It’s a core part of Facebook’s front-end development, particularly for building dynamic, interactive user interfaces. The creation and ongoing development of React by Facebook have been instrumental in its evolution and popularity in the broader web development community. Facebook’s use of React serves as a significant real-world example of the library’s capabilities in handling complex, large-scale applications.
3. Is Instagram built with React Native?
Yes, Instagram has incorporated React Native into its application. React Native, developed by Facebook (now Meta Platforms, Inc.), enables developers to build mobile apps using the same design as React, allowing for shared code elements between web and mobile platforms. Instagram’s use of React Native is part of its strategy to improve app development efficiency and consistency across platforms.
This approach allows for a more unified and streamlined development process, leveraging the advantages of React Native, such as live reloading and a single codebase for both iOS and Android platforms.
4. Is Netflix built using React?
Yes, Netflix is built using React for its web application’s user interface. React’s efficiency in managing dynamic content and user interactions makes it ideal for Netflix’s needs, ensuring a smooth and responsive experience for viewers. React’s component-based architecture also allows for scalable and maintainable code, which is essential for a service as widely used and constantly evolving as Netflix. This approach enables them to manage and update their platform efficiently, catering to millions of users worldwide.
5. What does Netflix use for frontend?
For its front-end, Netflix primarily uses React, a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
- React: A JavaScript library for building user interfaces, React is the core technology used in Netflix’s front-end development. It enables efficient rendering and management of dynamic user interfaces.
- JavaScript and CSS: Alongside React, standard web technologies like JavaScript and CSS are used for scripting and styling.
- Other Supporting Libraries: Netflix also integrates various other JavaScript libraries and frameworks to complement React’s capabilities, enhancing functionality and user experience.
This combination ensures a dynamic, responsive, and engaging user experience for Netflix’s streaming service.
6. Is YouTube built on Angular or React?
No, YouTube’s main web application is not built on Angular or React. It primarily uses Polymer, a JavaScript library for building web applications with Web Components. YouTube TV, a different product, uses React for its development. Angular is not the primary framework for YouTube’s main web interface.
Framework Future and Trends
As we wrap up our exploration of the ever-shifting landscape of web development frameworks, one thing becomes abundantly clear: change is the only constant. ReactJS, Angular, Vue.js, and the like – these are not static entities, but vibrant ecosystems in perpetual flux.
So, what does the future hold for these frameworks, and for web development as a whole? Here are a few key takeaways to ponder:
1. The Rise of Hybrid Approaches:
Gone are the days of rigid allegiance to a single framework. Developers are increasingly embracing a “best tool for the job” mentality, mixing and matching technologies to craft bespoke solutions. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of different frameworks, like ReactJS’s component-based architecture for UI and Angular’s robust data binding for complex applications.
2. The Allure of Low-Code/No-Code:
The democratization of web development is well underway, with low-code/no-code platforms gaining traction. These platforms offer visual drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built components, allowing even non-programmers to build basic web applications. While not a direct threat to established frameworks, these tools can serve as entry points, potentially feeding the developer talent pool in the long run.
3. The AI Integration Imperative:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic buzzword; it’s rapidly becoming an essential tool for developers. Frameworks are incorporating AI features like code completion, automated testing, and even AI-powered design assistance. This trend is poised to revolutionize the development process, making it faster, more efficient, and potentially more creative.
4. The Ongoing Security Saga:
Web security remains a top concern, and frameworks are constantly evolving to address new vulnerabilities. Expect to see increased focus on secure coding practices, built-in security features, and integration with security tools within frameworks themselves.
5. The Community Reigns Supreme:
The open-source nature of these frameworks is one of their greatest strengths. Vibrant communities of developers contribute, innovate, and troubleshoot, ensuring the frameworks stay relevant and cutting-edge. This collaborative spirit is what propels the web forward, and it’s something to celebrate.
As we stand at the precipice of the future, one thing is certain: the web development landscape will continue to evolve at a breakneck pace. But fear not, fellow developers! By embracing change, staying curious, and honing our skills, we can navigate these exciting times and continue to build amazing things for the web.
Remember, the best framework is the one that empowers you to create, to solve problems, and to push the boundaries of what’s possible. So, keep exploring, keep learning, and keep building. The future of the web is bright, and it’s in our hands to shape it.