In this Salesforce tutorial for beginners, you will learn Salesforce from scratch. This tutorial will guide you through the foundational elements of Salesforce architecture, exploring its core components and functionalities.
In this tutorial, we will discuss the following topics:
- What is Salesforce?
- History of Salesforce
- Why Should We Learn Salesforce?
- Salesforce CRM
- What is SFDC?
- Salesforce Benefits
- Features of Salesforce
- Salesforce Products
- How Do We Access Salesforce?
- Why Should We Choose Salesforce?
- Why is Salesforce Gaining Popularity?
- Differences Between Salesforce CRM and Dynamic CRM
- Cloud Computing
- Differences Between the Services and Components Managed by IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
- Problems with Traditional Software Methodology (Legacy Platforms)
What is Salesforce?
Salesforce is a leading cloud-based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform designed to help businesses manage customer information, interactions, and processes more effectively. It serves as a central platform for various business functions, including sales, customer service, marketing, and more, enabling organizations to streamline their operations and enhance communication across teams.
Salesforce as a Cloud-Based Platform
As a cloud-based platform, Salesforce provides businesses with the flexibility and accessibility to manage and analyze customer activities and data from anywhere in the world. This means that teams can collaborate in real-time, regardless of their physical location.
The platform’s cloud nature ensures businesses can scale their operations efficiently without requiring extensive hardware installations or maintenance, leading to lower IT costs and higher adaptability.
Salesforce’s cloud infrastructure also offers robust security features, ensuring sensitive customer data is securely managed and compliant with industry standards.
History of Salesforce
Salesforce was founded in 1999 by Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez as a company specializing in software as a service (SaaS). It started with the vision of making software easier to purchase, simpler to use, and more democratic without the complexities of installation, maintenance, and constant upgrades.
Salesforce introduced its new flagship product, Salesforce Automation (SFA). It revolutionized how companies managed customer relationships and sales processes, moving from the traditional client-server model to a centralized, web-based service.
Milestones and Innovations
Over the years, Salesforce has expanded its product line and introduced significant innovations that have shaped the CRM industry.
Key milestones include:
- 2004: Salesforce went public on the New York Stock Exchange under the CRM ticker, raising significant capital to fuel its growth.
- 2006: The AppExchange, a marketplace for third-party applications that integrate with Salesforce, was introduced, marking a pivotal step in creating a comprehensive ecosystem around its products.
- 2011: Salesforce Chatter was launched, enhancing productivity and collaboration among users with features like social networking and instant messaging integrated within their CRM environment.
- 2013: The release of Salesforce1, a mobile-initiative app, reflecting Salesforce’s commitment to mobile CRM solutions.
- 2014: The Salesforce Customer Success Platform was announced, an integrated solution that combined Salesforce’s analytics, community, service, sales, marketing, and app-building capabilities.
- 2016: Salesforce introduced Einstein, an AI layer built into the Salesforce platform, providing AI capabilities across all Salesforce clouds and enhancing data insights and decision-making processes.
- 2019: Acquisition of Tableau, a significant move to expand Salesforce’s data visualization and business intelligence capabilities.
- 2020: Salesforce was ranked #1 in CRM for the seventh consecutive year by IDC and expanded its pandemic response with the launch of Salesforce Care, Work.com, and Vaccine Cloud. It was added to the Dow Jones Industrial Average, acquired Vlocity, and announced plans to acquire Slack. It also hosted a virtual Dreamforce with over 140 million views.
- 2021: Salesforce completed its acquisition of Slack, promoting a new vision for a Slack-driven Digital HQ, introduced Salesforce+, achieved Net Zero emissions, sourced 100% renewable energy, and committed to new Equality initiatives and police reform.
- 2022: Salesforce announced the Customer Data Cloud at its 20th Dreamforce, launched the Safety Cloud and NFT Cloud, and was recognized as the Most Sustainable Company and World’s Best Workplace, reinforcing its commitment to sustainability and excellence.
- 2023: Salesforce’s Einstein made over 1 trillion AI-powered predictions weekly, and the company launched Einstein GPT, the Einstein 1 Platform, and Einstein Copilot. Salesforce Ventures also announced a $500 million generative AI fund, and the company continued its significant philanthropic efforts through the 1-1-1 model.
Why Should We Learn Salesforce?
Career Opportunities
Learning Salesforce opens up many career opportunities in various sectors due to its widespread adoption across industries. As the leading CRM platform globally, Salesforce expertise is highly valued in job markets, with roles ranging from Salesforce administrators and developers to project managers and IT consultants.
Professionals skilled in Salesforce can expect competitive salaries and strong demand for their skills as companies continue to enhance their customer relationship management systems.
Salesforce offers a robust certification program that helps further validate your skills and can significantly enhance your employability and career progression.
Industry Adoption and Ecosystem
Salesforce is widely adopted across industries ranging from technology and healthcare to finance and manufacturing. Still, it also boasts a vast ecosystem that includes third-party apps, consultants, and developers.
This ecosystem continually evolves, fueled by constant innovation and integration that keep the platform at the cutting edge of technology and business needs. The widespread adoption is also a testament to the platform’s scalability and flexibility, accommodating businesses of all sizes and varying requirements.
This pervasive use creates a dynamic market for Salesforce solutions and a community of users and developers, contributing to a vibrant support network and an extensive resource pool of knowledge and tools. Learning Salesforce provides technical skills and access to a thriving network and community, enhancing professional growth and networking opportunities.
Salesforce CRM
Core Components of Salesforce CRM
Salesforce CRM is built on several core components that provide a comprehensive toolset for managing customer relationships effectively.
These include:
- Sales Cloud: It manages sales processes, tracks customer interactions, and automates business workflows to increase sales productivity.
- Service Cloud: It delivers personalized customer service with features for managing cases, automating service processes, and creating self-service customer portals.
- Marketing Cloud: This service enables tailored marketing campaigns across multiple channels, providing tools for email marketing, social media campaigns, and digital advertising.
- Commerce Cloud: It supports e-commerce for B2C and B2B environments, integrating customer data for a unified shopping experience.
- Analytics Cloud: It provides powerful data visualization tools and analytics capabilities to make data-driven decisions.
- Community Cloud: It allows companies to create branded sites connecting customers, employees, and partners with each other and the data they need.
- Salesforce Platform: It enables custom application development on the Salesforce ecosystem.
How Salesforce CRM Stands Out
Salesforce CRM distinguishes itself in the competitive CRM market through several key aspects:
1. Customer 360
It is an integrated CRM platform that connects Salesforce products, giving a unified customer view across sales, customer service, marketing, and more. This integration ensures that all teams access the same data, providing a consistent and informed customer experience across all touchpoints.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Salesforce’s cloud-based structure allows businesses of any size to scale up or down based on their needs without significant upfront costs. The platform’s extensive customization capabilities through declarative and programmatic tools allow it to adapt to specific business requirements.
3. Ecosystem and Marketplace
Salesforce’s AppExchange marketplace features thousands of third-party applications that extend the functionality of Salesforce CRM in countless ways. This vibrant ecosystem also includes a global community of developers, administrators, and consultants who continuously drive innovation and share best practices.
4. Continuous Innovation
Salesforce is known for its rapid innovation cycles. It regularly introduces new features and technologies that keep the platform at the forefront of CRM and technology trends like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain.
5. Commitment to Social Responsibility
Beyond its technical capabilities, Salesforce is also recognized for its commitment to social issues, emphasizing trust, customer success, innovation, and equality as core values that drive its corporate decisions and culture.
These features make Salesforce CRM a powerful tool for managing customer relationships and a dynamic platform that pushes the boundaries of what CRM software can achieve.
What is SFDC?
SFDC stands for Salesforce.com, the original domain and current company name that hosts the Salesforce platform. SFDC is a cloud-based CRM software and enterprise cloud ecosystem that helps businesses manage customer relationships, streamline processes, and improve profitability in a scalable, customizable platform.
It offers comprehensive services, including sales management, customer service, marketing automation, and business analytics, all accessible online. This setup allows users to work efficiently without needing to install local software, offering global accessibility and real-time collaboration capabilities.
Relation Between SFDC and Salesforce
SFDC and Salesforce are essentially two terms referring to the same entity. SFDC is the platform, while “Salesforce” is the company that provides the platform.
However, in common usage, Salesforce refers to the entire range of products and services offered by Salesforce.com, Inc., which extends beyond the basic CRM functionalities to include a broad suite of enterprise applications focused on customer service, marketing automation, analytics, and application development connected through a single, integrated cloud computing platform.
This platform allows developers to create and deploy custom applications that leverage SFDC’s core functionalities, making Salesforce synonymous with innovative cloud solutions beyond traditional CRM services.
Why SFDC?
Benefits Over Traditional CRM Systems
SFDC (Salesforce.com) offers numerous advantages over traditional CRM systems, primarily due to its cloud-based architecture. This modern approach eliminates the need for substantial initial hardware investments and complex software maintenance, typical requirements of traditional on-premise CRM systems.
With SFDC, updates are automatic and frequent, ensuring all users can access the latest features and security enhancements without downtime or additional costs.
The cloud-based system allows for greater scalability and flexibility, enabling businesses to adjust their usage based on growth and changing needs without significant disruptions or infrastructure changes.
Specific Advantages of SFDC
- Accessibility: SFDC provides access to the CRM system from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and real-time data access for a globally distributed workforce.
- Integration Capabilities: With its extensive API and a large ecosystem of integration partners, SFDC can be seamlessly integrated with various other software and platforms, enhancing its functionality and allowing for a more connected enterprise system.
- Customization and Scalability: SFDC’s platform is highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor the CRM to fit their specific processes and needs. As a business grows, Salesforce can scale alongside it, making adjustments easily without significant cost.
- Robust Security: Leveraging enterprise-grade security features, SFDC protects sensitive data and complies with a range of international regulatory standards, giving businesses confidence in the integrity and security of their data.
Traditional CRM Vs. Salesforce CRM
Key Differences in Functionality
- Deployment: Traditional CRMs are often deployed on-premise, requiring physical servers and ongoing maintenance by the company’s IT staff. In contrast, Salesforce CRM is entirely cloud-based, with all infrastructure managed by Salesforce, reducing the IT burden on the company.
- Custom Development: While traditional CRMs can be customized, they often require extensive coding and are limited by the underlying platform capabilities. Salesforce CRM offers a more flexible environment with its own development language (Apex) and platform (com), designed for rapid development and customization.
Comparison of User Experience
- User Interface: Salesforce CRM provides a modern, intuitive user interface that is continuously updated to reflect new trends and user feedback. Traditional CRM systems may have less frequent updates and can appear outdated, potentially leading to a steeper learning curve and lower user adoption rates.
- Mobile Experience: Salesforce CRM emphasizes mobile access, providing a robust mobile app allowing users to do nearly everything they can on a desktop. Traditional CRMs may offer limited mobile features, impacting the productivity of on-the-go employees.
- Collaboration Tools: Salesforce integrates various communication and collaboration tools, such as Salesforce Chatter, which enables users to collaborate seamlessly within the platform. Traditional CRMs might require third-party tools for similar functionality, complicating the user experience.
Salesforce Benefits
1. Comprehensive Solution
Salesforce provides a solution that covers sales, customer service, marketing, community management, analytics, and more, all within a single platform. This comprehensive coverage ensures that businesses can effectively manage all aspects of their customer relationships, from lead acquisition to ongoing engagement and support.
2. Cloud-Based Data Storage
Utilizing cloud-based data storage, Salesforce enables businesses to store vast data securely online. This approach enhances data security and compliance and allows users to access this data from anywhere in the world, facilitating remote work and real-time decision-making.
3. Versatility for All Business Sizes
Salesforce is designed to be flexible, catering to the needs of small businesses, mid-sized companies, and large enterprises alike. Its scalability and extensive range of products ensure that businesses of any size can tailor the platform to their specific requirements.
4. Pay-as-You-Go Service Model
Salesforce’s pay-as-you-go model makes it financially accessible for businesses of all sizes. Companies can start with what they need and expand services as their business grows, which helps them manage costs effectively without significant upfront investments.
5. Boosted Sales Productivity and Customer Loyalty
Salesforce automates many routine sales and customer management tasks, allowing sales teams to focus more on closing deals and less on managing data. The platform’s customer service tools also help improve customer satisfaction, boosting loyalty and retention.
6. Easy Integration with Third-party Apps
One of Salesforce’s strengths is its ability to seamlessly integrate with a wide range of third-party applications through its extensive API and partnerships. This flexibility allows businesses to connect Salesforce with other systems, creating a unified workflow and data system.
7. Scalability
Salesforce scales effortlessly with your business growth. Whether you’re adding new users, increasing data storage, or integrating new functionalities, Salesforce can accommodate this growth without redesigning the underlying systems.
8. Customization
With its powerful customization capabilities, Salesforce allows businesses to modify workflows, dashboards, and interfaces to meet their specific operational needs. Salesforce’s platform also supports custom app development, enabling companies to create unique solutions tailored to their business processes.
9. Community and Support
Salesforce boasts a robust community of users, developers, and partners known as the Trailblazer Community. This community is a valuable resource for support, learning, and networking. Salesforce provides extensive customer support and professional services to ensure users can maximize the value of their investment in the platform.
Features of Salesforce
1. Cloud-Based Advantage
Salesforce leverages cloud technology to offer businesses a reliable and scalable CRM solution without the typical overhead associated with physical servers and IT maintenance. This cloud-based advantage ensures users can access Salesforce from any device with an internet connection, providing flexibility and enhancing team collaboration.
2. Comprehensive CRM Features
Salesforce delivers a full spectrum of CRM functionalities, including sales management, customer service, marketing automation, and detailed analytics. This comprehensive approach ensures that all customer relations are managed in a unified platform, streamlining processes and improving data accuracy.
3. Integration Capabilities
The platform excels in integrating seamlessly with many other software systems and tools, whether through native integrations, APIs, or the AppExchange marketplace. This allows businesses to maintain a cohesive technology ecosystem that enhances productivity and data consistency.
4. Contact Management
Salesforce provides robust contact management capabilities that allow businesses to store, track, and manage contact details and customer interaction histories. This feature ensures teams have the context for personalized customer interactions and relationship building.
5. Marketing and Sales Lead
The platform supports advanced marketing and sales lead management tools that help businesses track the efficiency of their marketing campaigns and follow leads from generation to conversion. These tools are designed to optimize marketing strategies and boost sales performance.
6. Build and Run Innovative Apps
With Salesforce’s Platform, businesses can build and run custom applications directly within the Salesforce ecosystem. This flexibility allows companies to develop apps perfectly tailored to their specific needs, enhancing functionality without compromising security or performance.
7. Salesforce Analytics
Through comprehensive data analysis tools, Salesforce Analytics provides deep insights into business operations and customer behaviors. These tools help companies make informed decisions based on real-time data, leading to better business outcomes.
8. Sales Community
The Sales Community feature enables companies to connect their sales teams with other departments and external partners, facilitating collaboration and information sharing. This community-driven approach helps streamline processes and ensures all stakeholders are aligned on objectives.
9. Salesforce Engine
The Salesforce Engine is a powerful automation tool that drives the platform’s workflows, processes, and rules. It is designed to increase efficiency by automating routine tasks and orchestrating complex business processes.
10. Lead Management
Salesforce’s lead management system helps businesses track and nurture leads through customized paths, improving conversion rates and maximizing sales opportunities. It includes tools for scoring, tracking, and prioritizing leads to ensure that sales teams focus their efforts where they are most likely to yield results.
11. Partnership Management
Salesforce also offers tools to manage partnerships effectively, allowing businesses to track joint sales, manage leads shared between partners, and collaborate on marketing initiatives.
Salesforce Products
Overview of Salesforce Cloud Solutions
- Sales Cloud: It empowers sales teams by automating sales processes, enhancing lead tracking, and providing comprehensive tools for sales management, ultimately driving sales efficiency and productivity.
- Marketing Cloud: It delivers robust digital marketing capabilities, allowing marketers to create and manage marketing campaigns and customer journeys seamlessly across multiple channels.
- Service Cloud: It enhances customer service capabilities with tools for case management, customer self-service portals, and live agent support, all designed to improve customer satisfaction.
- Commerce Cloud: It supports both B2C and B2B commerce, streamlining e-commerce operations with integrated tools that enable personalized shopping experiences across digital channels.
- Experience Cloud: It allows organizations to build connected digital experiences for customers, partners, and employees, integrating data and personalizing interactions across various touchpoints.
- IoT Cloud: It connects internet-connected devices to Salesforce, automating actions based on real-time data and providing deeper insights into device usage and customer interactions.
- Analytics Cloud: It offers powerful data analysis tools and intelligent insights by leveraging artificial intelligence and big data, helping businesses make informed decisions based on comprehensive analytics.
- Health Cloud: Tailored specifically for healthcare providers, Health Cloud enables personalized patient care by providing a complete view of the patient journey, integrating clinical and non-clinical data, and facilitating collaboration among care teams.
Introduction to Platform Solutions
- Heroku: A cloud platform as a service (PaaS) supporting several programming languages, Heroku enables developers to build, run, and scale applications similarly across all programming languages.
- Tableau: Acquired by Salesforce, Tableau specializes in making data understandable to everyone through interactive, visual analytics, enhancing the ability to make data-driven decisions.
- MuleSoft: Another strategic acquisition by Salesforce, MuleSoft offers the leading platform for building application networks connecting apps, data, and devices with APIs.
How Do We Access Salesforce?
Accessing Salesforce Online
Salesforce can be accessed online through any web browser, providing users flexibility and ease of use.
To start using Salesforce, follow these steps:
- Visit the Salesforce Website: Go to the official Salesforce website (www.salesforce.com) and click on the ‘Login’ button located at the top right corner of the home page.
- Enter Your Credentials: If you already have an account, enter your login credentials (username and password) and hit ‘Log in.’ If you do not have an account, you can sign up for one by clicking on ‘Try for Free’ to create a new Salesforce trial account.
- Navigate the Interface: Once logged in, you will be directed to your Salesforce dashboard. Here, you can access various modules and data, customize your dashboard, and start working with the CRM tools available according to your role and permissions.
Salesforce also provides robust security features, ensuring all data is securely accessed and managed. Users can set up multi-factor authentication and other security measures to protect their accounts and sensitive business information.
Salesforce Mobile App
For on-the-go access, Salesforce offers a mobile app that brings the power of the Salesforce platform to your mobile device. The Salesforce Mobile App is available for download on Android and iOS devices and provides many of the same functionalities as the desktop version.
Here’s how you can get started:
- Download the App: Search for the Salesforce Mobile App in the Google Play Store or Apple App Store, and download it onto your mobile device.
- Log in to Your Account: Open the app and log in with the same credentials you use to access the online platform.
- Navigate Your CRM on the Go: The mobile app provides a user-friendly interface tailored for smaller screens. It allows you to manage leads, check dashboards, update opportunities, and communicate with your team members, all from your smartphone or tablet.
The Salesforce Mobile App ensures that users can stay connected and productive even when away from their desks. The app syncs data in real-time, so you always have access to the most up-to-date information, ensuring seamless workflow continuity regardless of your location.
Why Should We Choose Salesforce?
1. Business Benefits
Choosing Salesforce provides many business benefits, enabling organizations to enhance their customer relationship management, streamline processes, and boost overall productivity.
Salesforce’s comprehensive CRM solutions help businesses cultivate deeper relationships with customers, better understand their needs, and deliver exceptional service, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Technological Edge
Salesforce is at the forefront of CRM technology, continually evolving with the latest advancements. It incorporates cutting-edge features like artificial intelligence (AI) through Salesforce Einstein, as well as advanced analytics capabilities, offering businesses the tools they need to stay competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
3. Cloud-based Accessibility
The cloud-based nature of Salesforce allows users to access the platform from anywhere, at any time, using any device with internet connectivity. This flexibility is important for businesses with remote teams or those requiring access to real-time data outside of traditional office settings.
4. Affordability
Salesforce offers a range of pricing plans that cater to businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises. The pay-as-you-go model ensures that companies only pay for what they use, which helps in managing costs effectively while still benefiting from a robust CRM platform.
5. Versatile Capabilities
Whether it’s sales, marketing, service, or IT needs, Salesforce provides versatile capabilities to manage various aspects of business operations. This versatility allows companies to adapt the platform to their specific processes and workflows, creating a tailored experience that maximizes efficiency.
6. Simplified Setup
Salesforce is designed for ease of use, with a setup process that is straightforward and user-friendly. Organizations can quickly deploy Salesforce without the lengthy and complex implementation phases typically associated with traditional CRM systems.
7. No Software Installation
Being a cloud-based platform, Salesforce does not require any software installation. This simplifies the IT infrastructure and eliminates the need for ongoing software maintenance and updates, reducing the IT burden on staff.
8. Seamless Integration
Salesforce boasts extensive integration capabilities, connecting smoothly with other systems and applications through APIs and a robust marketplace of apps (AppExchange). This seamless integration extends the functionality of Salesforce, allowing businesses to create a fully integrated IT ecosystem.
9. User-friendly Interface
The Salesforce interface is designed with the user in mind, ensuring that it is intuitive and easy to navigate. This user-friendly design helps reduce the learning curve and allows users to become proficient quickly, enhancing productivity.
10. Cost Reduction
By automating and optimizing business processes, Salesforce helps reduce operational costs. Its analytics and reporting tools also allow businesses to make data-driven decisions that can lead to cost savings and improved resource allocation.
Why is Salesforce Gaining Popularity?
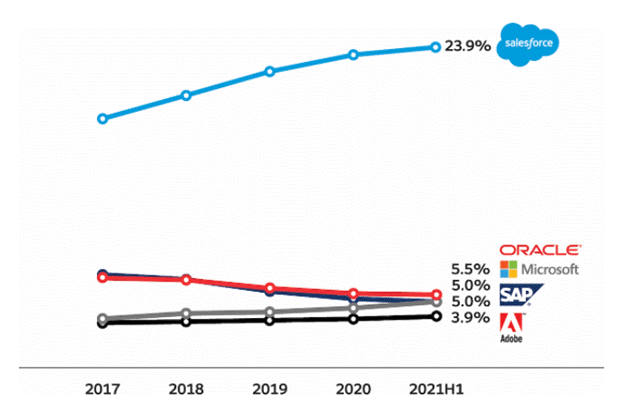
The below graph displays the market share trend for several major CRM companies from 2017 through the first half of 2021. Salesforce shows a notable upward trajectory, with its market share increasing consistently year over year, reaching 23.9% by the first half of 2021.
The data highlights Salesforce’s growing dominance and increasing preference in the CRM market relative to its competitors.
Market Trends
Salesforce has been aligning with major market trends emphasizing digital transformation, customer experience, and cloud computing. These trends have accelerated the adoption of CRM solutions that offer robust, cloud-based functionalities capable of managing vast amounts of data and customer interactions across multiple channels.
Salesforce’s leading position in the CRM market is reinforced by its continuous innovation and ability to integrate emerging technologies such as AI and IoT into its platform.
Reasons Why Salesforce is Gaining So Much Popularity
- Scalability and Customization: Allows businesses to expand and tailor their CRM to meet evolving needs, enhancing productivity and user experience.
- Multi-tenant Architecture: Ensures seamless, automatic updates and efficient resource use, reducing operational costs.
- Partner Ecosystem: Features a diverse network of partners, expanding capabilities with numerous third-party integrations.
- Data Security: Provides robust security across the platform, supported by comprehensive compliance certifications.
- Continuous Enhancement: Stays ahead of industry trends with regular updates and innovations, addressing new business challenges effectively.
Differences Between Salesforce CRM and Dynamic CRM
Platform Comparison
Salesforce CRM and Microsoft Dynamics CRM are two of the leading platforms in the CRM market, each with distinct strengths and focus areas:
1. Deployment Options
Salesforce primarily offers a cloud-based deployment, ensuring users have access to the platform and data anywhere and anytime. Microsoft Dynamics CRM provides more flexibility with cloud, on-premise, and hybrid deployment options, catering to businesses with specific data handling or regulatory requirements.
2. Customization and Flexibility
Salesforce stands out for its high degree of customization and an extensive app ecosystem through its AppExchange. Dynamics CRM also offers strong customization capabilities but is often noted for its native integration with other Microsoft products like Office 365 and Outlook.
3. User Interface and Usability
Salesforce features a user-friendly interface that is highly intuitive and easy to navigate, which can enhance productivity. Dynamics CRM integrates deeply with other Microsoft tools, offering a familiar interface for users already accustomed to the Microsoft environment.
4. Pricing Structure
Salesforce generally adopts a subscription-based pricing model that can scale with the features and number of users. Dynamics CRM may offer more flexible pricing options, which is especially attractive for companies looking for on-premise deployments or those already using multiple Microsoft products.
Use Case Scenarios
Both Salesforce and Dynamics CRM serve broad markets, but their features may cater to specific business needs differently:
- Enterprise vs. SMB: Salesforce is a strong fit for enterprises and SMBs alike, particularly excelling in scenarios where innovation and scalability in the cloud are priorities. Dynamics CRM is often favored by organizations that are heavily invested in Microsoft technologies and seeking deep integration with them.
- Industry Solutions: Salesforce offers solutions tailored to various industries, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more, with specialized products like Health Cloud. Dynamics CRM provides strong offerings for government, retail, and manufacturing sectors, leveraging Microsoft’s enterprise technology stack.
- Sales and Marketing: With robust analytics and marketing tools, salesforce shines in managing customer relationships across the entire customer lifecycle, from lead to loyalty. Dynamics CRM offers strong sales capabilities with advanced reporting features, benefiting from tight integration with Microsoft Power BI.
Cloud Computing
Types of Cloud Services
1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides fundamental computing, network, and storage resources on demand, over the Internet, and on a pay-as-you-go basis. Users have control over their virtual networking environment, including choice of operating system, development platform, and data hosting.
Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure.
2. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. The service provider centrally hosts and manages the service. SaaS eliminates the need for organizations to install and run applications on individual computers or in their own data centers.
Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace.
3. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
PaaS allows customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app. PaaS can be used for general software development, and services may include hosting, database management, security, and scalability.
Examples include Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Services.
4. Basics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing delivers different services through the Internet, including data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. Cloud-based storage makes it possible to save files to a remote database and retrieve them on demand.
The services are highly flexible, giving organizations the opportunity to scale up as their computing needs increase and scale down as demand decreases.
Importance in Today’s Technology Landscape
Cloud computing has become critical in today’s technology landscape because it enables flexibility, global scale, and faster innovation.
It allows businesses to:
- Reduce IT Costs: Moving to cloud computing may reduce the cost of managing and maintaining IT systems.
- Scalability: Cloud environments allow enterprises to operate more efficiently and adjust their resource use in response to demand.
- Accessibility and Collaboration: Since data is stored in the cloud, it can be accessed from any device in any part of the world. Teams in different locations can collaborate on projects without needing to duplicate files.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud computing can also enhance data security for its users by backing up data off-site, decreasing the potential for data loss.
Differences Between the Services and Components Managed by IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Service Model Comparison
1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
This model provides virtualized physical computing resources over the Internet. IaaS offers businesses the highest level of flexibility and management control over their IT resources. It is typically used for data storage, virtualization, networks, and servers.
- Key Components: Virtual machines, storage, networks, and servers.
- Common Uses: Hosting websites, data storage, backup, and web apps.
2. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a framework for developers to build upon and use to create customized applications. The enterprise can manage all servers, storage, and networking or a third-party provider, while the developers can maintain application management.
- Key Components: Development tools, database management systems, and business analytics.
- Common Uses: Application development, business analytics, and business process management.
3. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides a complete software solution you purchase on a pay-as-you-go basis from a cloud service provider. You rent the use of an app for your organization, and your users connect to it over the Internet, usually with a web browser. The underlying infrastructure, middleware, app software, and app data are in the service provider’s data center.
- Key Components: Web applications, APIs, SDKs.
- Common Uses: Email, customer relationship management (CRM), and collaboration tools.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Needs
1. Assessing Business Requirements
Identify specific business needs such as resource availability, budget, existing IT infrastructure, and technical expertise. This assessment helps you decide which cloud service would best integrate with your business.
2. Scalability Needs
Consider whether your business requires the ability to scale resources up or down as needed. IaaS offers high scalability, which is advantageous for businesses with fluctuating workloads. PaaS and SaaS offer scalability but are typically more restrictive than IaaS.
3. Control and Customization
Determine the level of control and customization you need over your applications and data. IaaS offers the most control, making it suitable for businesses that need a highly customized environment. PaaS provides control over application deployment and management, whereas SaaS offers the least control, suitable for businesses looking for ready-to-use applications.
4. Security and Compliance Requirements
Analyze your security needs and any regulatory compliance requirements affecting your data. While all cloud models offer robust security features, the level of security control varies. IaaS allows the most detailed security management, whereas SaaS might be preferable for businesses that are satisfied with the security measures provided by the vendor.
5. Cost Efficiency
Consider your budget and how each model can optimize your spending. IaaS generally incurs costs based on actual usage, while PaaS and SaaS typically have a fixed cost but differ in terms of additional features and scale options.
Problems with Traditional Software Methodology (Legacy Platforms)
Steps in Traditional Software Development
In the conventional software development methodology, organizations must navigate a series of time-consuming and costly steps to create an application:
- Formation of an Idea: The process begins with conceptualizing the application’s goals, functionality, and target user base.
- Buying and Setting Up Hardware: Significant upfront investments are required to purchase and set up physical servers and other hardware necessary to support the software.
- Installing Software: Installation of the base software platforms needed to develop and run the application, which often includes dealing with multiple vendor licenses and software compatibility issues.
- Defining Users and Providing Accesses: Configuring the software to define user roles and access permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access certain data or functionalities.
- Setting Up Means for Reporting and Analytics: Integrating or developing tools for data analysis and reporting capabilities to monitor the application’s performance and user interactions.
- Building Security Around the Application: Implementing security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems to protect the application and its data.
- Making the Application Mobile Phone Accessible: Ensuring the application is optimized for mobile devices may require additional development and testing.
Limitations of Legacy Systems
Traditional software methodologies often suffer from several limitations that can hinder business agility and innovation:
- Costly Maintenance and Upgrades: Legacy systems require ongoing maintenance and periodic upgrades, which can be both disruptive and expensive.
- Lack of Scalability: Scaling a traditional setup to handle increased loads typically involves purchasing additional hardware and may result in significant downtime.
- Inflexibility: Making changes or updates to legacy systems can be slow and complex, often requiring system downtime or extensive coding.
- Security Risks: Older systems may not be updated with the latest security patches or support modern security protocols, making them vulnerable to newer threats.
Transitioning to Modern Solutions like Salesforce
Moving to modern solutions such as Salesforce can address many of the drawbacks associated with traditional software methodologies:
- Cloud-Based Model: Salesforce operates on a cloud-based platform that eliminates the need for physical hardware and associated capital expenditures. This model also facilitates immediate updates and upgrades without downtime.
- Scalability and Flexibility: With Salesforce, businesses can easily scale their operations up or down based on demand without significant upfront costs. The platform’s extensive customization capabilities allow for rapid adaptation to new business requirements.
- Enhanced Security: Salesforce provides robust security measures that are continuously updated to handle emerging threats, ensuring that data remains secure and compliance with regulatory standards is maintained.
- Accessibility and Integration: Salesforce is cloud-based, accessible from anywhere on any device, and integrates seamlessly with other applications, improving workflow efficiency and data consistency.