IT Staff Augmentation
In this guide to IT Staffing Augmentation, we’ll explore the fundamental concept of augmenting your IT workforce and the substantial advantages it offers for organizations in today’s dynamic tech environment.
Table Of Content
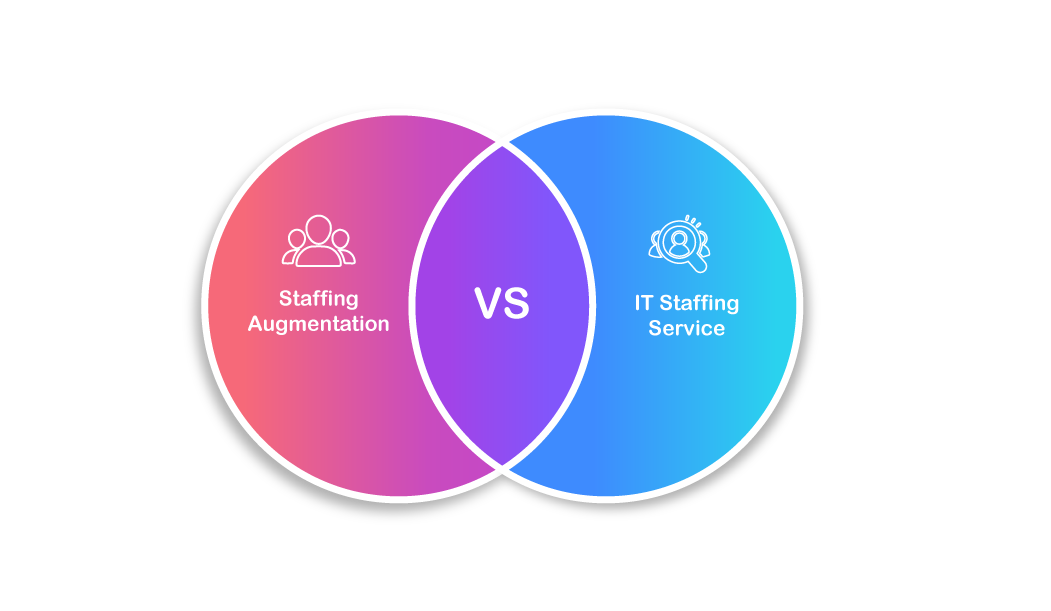
Staffing Augmentation vs IT Staffing Services
“Staff augmentation” and “IT staffing” are terms that are often used interchangeably, but it’s important to note that they refer to distinct methods of hiring IT professionals. While there may be some overlap between the two, understanding the differences can help you determine which approach is best suited to your company’s needs.

Staffing augmentation is a business model where external talent, usually on a contract or temporary basis, is hired to work alongside an organization’s existing staff. The external talent is hired to fill a specific skill gap in the organization or to handle a temporary increase in workload. Staff augmentation can be used to supplement a company’s workforce for a short-term project, or to provide expertise in a particular area where the company’s in-house skills are lacking. The external staff works on the client’s premises, using their tools and resources, and follows their processes and procedures. They are not responsible for the outcome of the project but rather provide additional resources to help the internal team.
On the other hand, IT staffing services refer to a more comprehensive approach to hiring IT talent. With IT staffing services, a third-party provider assumes responsibility for recruiting, hiring, and managing a team of IT professionals to support a client’s specific needs. This team can be located either on-site or off-site, and the provider is responsible for managing the team’s performance and delivering results.
In summary, staff augmentation is a short-term solution for filling specific skill gaps in an existing team, while IT staffing services are a more comprehensive approach to hiring and managing IT talent for a specific project or ongoing needs.
Staffing Augmentation vs Managed Services
There are two primary models that businesses can use to bring in external resources for support in their operations: staffing augmentation and managed services. Although these models share some similarities, there are several key differences between them.
Managed services involve outsourcing the management of specific functions or operations to an external service provider. The provider takes on responsibility for delivering and managing the service, providing the necessary tools, resources, and staff to complete the job. Managed services may encompass IT management, infrastructure management, and other business functions. The service provider is accountable for the project outcome, and the client pays a fixed fee for the services provided.
The primary benefit of managed services is the access to a pool of resources at a significantly lower cost than hiring your own team. This option works well when there is a need for highly skilled IT resources but not enough work to fill multiple full-time positions. However, the managed service provider typically charges a premium for these resources. Thus, as your needs grow, it can become more cost-effective to leverage staffing augmentation or direct hiring services.
IT Staffing Augmentation Industry
The IT job market is one of the fastest-growing job markets in the world, with an estimated 682,800 new jobs to be added between 2021 and 2031. The IT industry has experienced massive employment growth over the past decade and is expected to continue in the foreseeable future. With the advent of new technologies, businesses are increasingly relying on IT services, which has resulted in a significant demand for IT talent.

In the latter part of last month, a research study conducted by Lensa, a job search website, revealed that “computer occupations” are highly sought-after jobs in the United States, ranking second only to “health diagnostic and treatment practitioners.” Over 3.1 million individuals showed interest in available IT job positions by clicking on them, as reported by Lensa.
However, the IT talent shortage is becoming a major challenge for companies. This has led to the trend of outsourcing IT staffing services to staffing agencies. Companies are now opting to hire IT staffing agencies to handle their staffing needs. These agencies specialize in IT staffing and IT staffing augmentation, have a pool of skilled IT professionals, and can quickly provide the right talent for their clients’ needs.
Keeping up with the latest IT staffing industry news and reports is important for IT staffing professionals. The industry is always evolving, and staying informed of trends and changes can provide a competitive advantage. Reports can provide insights into market trends, growth opportunities, and potential challenges.
Download Whitepaper
Enter the email where we can send the whitepaper.
Staffing Augmentation vs Outsourcing
Staff augmentation and outsourcing are two approaches that organizations use to address their staffing needs. Both methods offer benefits, but they differ in terms of their level of control and involvement in the staffing process. Staff augmentation refers to the practice of hiring additional staff to work alongside an existing team to support a project or meet a short-term need. This approach allows organizations to scale their teams up or down as needed without making a long-term commitment. Staff augmentation can be used to fill gaps in expertise or skill sets, provide additional resources during peak periods, or support a specific project.

Outsourcing, on the other hand, involves hiring an external company to take over certain functions or processes. This can range from outsourcing a single task, such as payroll processing, to outsourcing an entire department, such as IT or customer service. Outsourcing is often used to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and gain access to specialized expertise.
The key difference between staff augmentation and outsourcing is the level of control and involvement that the organization has over the staffing process. With staff augmentation, the organization retains full control over the project or function, and the additional staff work alongside the existing team under the organization’s direction. In contrast, outsourcing involves delegating the responsibility for a function or project to an external company, which manages the work independently.
There are advantages and disadvantages to both approaches. Staff augmentation allows organizations to maintain control over their projects and retain their corporate culture while gaining additional resources.
Outsourcing, on the other hand, can provide access to specialized expertise and reduce costs, but it requires relinquishing some control over the process.

What are the types of IT Staffing Augmentation?
There are several types of IT staffing augmentation that an organization can consider:

Long-term augmentation
This involves bringing in external talent on a long-term basis, typically for more than six months, to address ongoing or recurring IT needs.

Skill-based augmentation
This involves bringing in external talent with specific skills or expertise, such as cybersecurity or cloud computing.

Short-term augmentation
This involves bringing in external talent on a short-term basis, typically less than six months, to address a specific need or project.

Project-based augmentation
This involves bringing in external talent for a specific project or initiative, such as a software development project or implementation of a new IT system.

Full-time augmentation
This involves bringing in external talent on a full-time basis, either as a contract worker or permanent employee, to address ongoing IT needs or to supplement in-house teams.
Key Benefits of Staffing Augmentation
There are several types of IT staffing augmentation that an organization can consider:

Access to a pool of IT talent with various backgrounds, skill sets, and level of experience.

Ability to virtually “test drive” prospective IT employees before making final hiring decisions.

Faster turnaround time on hiring because Pumex takes the time necessary to understand what you truly need in terms of background and skill set.

Ability to work directly with a dedicated IT staffing specialist throughout the entire procurement process.

Reduce operational costs by hiring temporary resources to augment existing in-house IT terms for short timeframes.

Increase staffing flexibility by reducing employee resources as projects come.

Access to a pool of IT talent with various backgrounds, skill sets, and level of experience.

Ability to virtually “test drive” prospective IT employees before making final hiring decisions.

Faster turnaround time on hiring because Pumex takes the time necessary to understand what you truly need in terms of background and skill set.

Ability to work directly with a dedicated IT staffing specialist throughout the entire procurement process.

Reduce operational costs by hiring temporary resources to augment existing in-house IT terms for short timeframes.

Increase staffing flexibility by reducing employee resources as projects come.
When does it make sense to use staffing augmentation?
Staff augmentation makes sense when an organization has a specific project or initiative that requires specialized IT skills or expertise that the in-house team does not possess. Here are some situations where staff augmentation can be a good solution:
Temporary spikes in workload
If a project requires a higher workload than the in-house team can handle, staff augmentation can be used to provide extra resources for a temporary period.
Lack of specialized skills
If a project requires a specific skill set that is not available in-house, staff augmentation can be used to bring in a specialist for a short period of time.
Short-term projects
If a project is expected to be completed in a short period of time, it may not be cost-effective to hire a full-time employee. Staff augmentation can provide the required skills for the duration of the project.
Budget constraints
Staff augmentation can be a more cost-effective solution than hiring a full-time employee with a specialized skill set. Especially when taken into consideration the overhead, fringe benefits, and expectation of long-term employment when hiring employees.
Test the waters before hiring
Staff augmentation can provide an opportunity for an organization to evaluate a potential employee's skills and fit within the organization before making a permanent hire.
Flexibility
Staff augmentation provides organizations with the flexibility to adjust the size of their team quickly and efficiently, without the long-term commitment of hiring full-time employees.
Knowledge transfer
Staff augmentation can also provide an opportunity for knowledge transfer from external specialists to in-house teams, improving the overall skill level of the organization.
Rapid response to changing needs
In the rapidly evolving field of IT, organizations may need to adapt quickly to new technologies or business needs. Staff augmentation can provide the necessary skills and expertise to respond to these changes in a timely manner.
Geographical diversity
If an organization is looking to expand into a new geographic region, staff augmentation can provide access to local talent without the need to establish a physical presence in the area.
Scalability
Staff augmentation can help organizations scale their IT operations quickly and efficiently, without the need to invest in additional resources.
Risk management
Staff augmentation can help mitigate risk by providing specialized expertise for critical projects or initiatives, reducing the potential for errors or delays.
Expertise in emerging technologies
Staff augmentation can provide access to specialized expertise in emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, or cloud computing, which may not be available in-house.
Faster time-to-market
Staff augmentation can help organizations bring products and services to market faster by providing access to specialized skills and expertise that may not be available in-house.
Capacity management
Staff augmentation can help organizations manage their IT capacity more effectively by providing additional resources during peak periods, without the need to hire additional full-time employees.
Focus on core business
By outsourcing IT talent needs to external providers, organizations can focus on their core business activities, rather than spending time and resources on IT staffing and management.
Employee retention
Staff augmentation can help organizations retain their existing employees by providing them with access to specialized training and development opportunities that may not be available in-house.
Diversity and inclusion
Staff augmentation can help organizations improve diversity and inclusion within their IT teams by providing access to talent from a range of backgrounds and geographic regions.
Continuity of service
Staff augmentation can provide continuity of service for critical IT functions during periods of employee turnover, ensuring that key processes and projects continue to run smoothly.
Access to new markets
Staff augmentation can provide access to new markets by providing access to local talent and expertise in different geographic regions.
Improved customer satisfaction
Staff augmentation can help organizations improve customer satisfaction by providing access to specialized skills and expertise that can improve product and service offerings.
In summary, staff augmentation can provide a range of benefits for organizations, from employee retention and diversity and inclusion to continuity of service and access to new markets. By leveraging external talent on an as-needed basis, organizations can optimize their IT operations and achieve their strategic objectives.
Download Whitepaper
Enter the email where we can send the whitepaper.
IT Staffing Augmentation Process
The IT staffing augmentation process typically involves several steps, which may vary depending on the agency or organization. Here are the general steps of the IT staffing process:
Identifying staffing needs
The first step is to determine the roles and skill sets required to fill the IT positions. This involves consulting with department heads or project managers to identify their staffing needs.
Job posting and sourcing candidates
The next step is to post job listings on job boards or other platforms, as well as reaching out to potential candidates directly. This could involve using recruiting agencies or leveraging existing networks.
Candidate screening
Once a pool of candidates has been identified, the next step is to screen candidates to assess their qualifications and fit for the role. This may involve reviewing resumes, conducting phone or video interviews, and administering technical assessments.
Interviewing
The next step is to schedule in-person or virtual interviews with candidates to further evaluate their skills and fit for the role. This may involve multiple rounds of interviews with different stakeholders.
Reference and background checks
Before making a job offer, it’s important to conduct reference and background checks on the top candidates to ensure they have a good track record and are a good fit for the company culture.
Job offer and negotiation
Once the top candidate has been identified and reference and background checks have been completed, the next step is to extend a job offer. This may involve negotiating salary and benefits packages.
Onboarding
The final step is to onboard the new employee, which may involve providing training, setting up equipment and access to systems, and introducing the employee to key stakeholders.
Throughout the IT staffing process, it is important to maintain effective communication with the candidate to ensure a positive candidate experience and to keep them informed about the status of their application.
IT Staffing Plan
Before you start hiring, it’s important to have a plan in place. A well-crafted staffing plan should include your organization’s goals, an assessment of your current workforce, and a timeline for hiring new staff. By having a clear plan, you can ensure that your IT staff aligns with your overall business strategy.
IT Staffing Strategy
Your staffing strategy should focus on finding the best candidates for your organization. This may involve using different staffing models, such as contract, contract-to-hire, or direct hire placements. Your staffing strategy should also include best practices for screening and interviewing candidates, as well as metrics for measuring success.
IT Staffing Models
Different staffing models can provide flexibility and cost savings, depending on your organization’s needs. Contract staffing involves hiring temporary workers for a specific project or time period. Contract-to-hire allows you to test out a worker before making a permanent hiring decision. Direct hire involves hiring an employee for a full-time position.
IT Staffing Best Practices
Some key best practices for IT staffing include creating a strong employer brand, developing an effective screening process, and providing clear job descriptions. It’s also important to ensure that your hiring process is fair and non-discriminatory.
IT Staffing Metrics
Measuring the success of your IT staffing process is important for identifying areas of improvement. Metrics may include time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, and retention rates. By tracking these metrics, you can continuously improve your hiring process.
IT Staffing Challenges
The IT staffing process is not without its challenges. Some common challenges include a shortage of qualified candidates, a competitive job market, and changing technology needs. By anticipating these challenges and having a solid plan in place, you can overcome them and find the right talent for your organization.
IT Staffing Trends
Keeping up with the latest trends in IT staffing is important for staying ahead of the curve. Some current trends include an increased focus on diversity and inclusion, a shift towards remote work, and a need for IT professionals with both technical and soft skills.
Staffing Augmentation Challenges
While staff augmentation can offer many benefits to organizations, such as flexibility and increased resources, it can also present some challenges. Here are some strategies to help organizations get around these challenges:
Communication:
One of the most significant challenges of staff augmentation is communication. It can be challenging to integrate new team members into an existing team, especially if they are working remotely. To overcome this challenge, it is essential to establish clear communication channels and ensure that everyone is on the same page. This can include regular team meetings, daily check-ins, and the use of collaboration tools.
Onboarding:
Another challenge of staff augmentation is onboarding new team members. It can be challenging to get new hires up to speed quickly, especially if they are only working on a short-term project. To address this challenge, it is essential to have a well-defined onboarding process that includes training, access to necessary tools and resources, and clear expectations for the role.
Cultural fit:
Staff augmentation can also present challenges in terms of cultural fit. It can be difficult to integrate new team members into an existing team culture, especially if they are only working on a short-term project. To overcome this challenge, it is important to select team members who have a similar work style and values as the existing team. Additionally, it can be helpful to involve existing team members in the selection process to ensure a good fit.
Quality control:
Maintaining quality control can also be a challenge in staff augmentation. It can be difficult to ensure that all team members are working to the same standards, especially if they are working remotely. To address this challenge, it is essential to establish clear quality control processes and provide regular feedback to team members.
Integration:
Integrating new team members into an existing team can be a challenge. It can be challenging to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals and that there is no duplication of effort. To address this challenge, it is important to establish clear roles and responsibilities and ensure that everyone understands how their work contributes to the overall project.
Security:
Security is an important challenge that organizations must consider when implementing staff augmentation. With more team members working remotely, there is an increased risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. To address this challenge, it is important to establish clear security protocols and ensure that all team members are following them. This can include using secure communication channels, enforcing strong passwords, and limiting access to sensitive data.
Download Whitepaper
Enter the email where we can send the whitepaper.
Staffing Augmentation Challenges
Location

Onsite

Offsite

Onshore

Nearshore (time zone aligned)
Engagement

Contract Basis

Direct Hire

Temp-to-perm Hire

Temporary Position

Permanent Position
Billing

Fixed Price

Tme and Materials

Team Augmentation

Outstaffing / Outsourcing
Key Staff Augmentation
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, IT professionals must continually update their skills and knowledge to stay relevant and competitive. Ensuring the candidates provided for your staff augmentation program have the relevant skills and certifications will be key to the success of your program. Here are some of the essential IT skills and certifications that are currently in demand:
IT Skills in Demand:
Cloud Computing:
With the increasing popularity of cloud-based services, professionals with skills in cloud computing are highly sought after. Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to store, manage, and process data on remote servers, rather than on their own local servers or computers. Cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are becoming increasingly popular, and IT professionals who are knowledgeable in these platforms are in high demand. According to a report by ReportLinker, the public cloud services market is expected to reach $987.7 billion by 2027. This significant growth in the cloud computing market is driving the demand for IT professionals skilled in cloud computing platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. In fact, a study by Indeed found that job postings for AWS skills increased by 232% between 2014 and 2019.
Cybersecurity:
With the rise of cyber threats, cybersecurity has become a top priority for businesses. IT professionals with skills in security operations, threat intelligence, and risk management are in high demand. Cybersecurity involves protecting networks, devices, and sensitive information from unauthorized access or attack. As businesses continue to move towards digitalization, the demand for cybersecurity professionals is expected to increase.
According to a report by The Global Risk Report 2023, cybercrime is expected to cost businesses $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This staggering figure highlights the importance of cybersecurity in today’s digital world. The demand for cybersecurity professionals is high, with a projected job growth rate of 31% from 2019 to 2029, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Data Science:
With the rise of big data, data science has become an essential skill for businesses to gain insights into customer behavior and market trends. Data science involves analyzing large datasets to extract valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. Professionals with skills in data analysis, statistics, and machine learning are in high demand. They help businesses make sense of large datasets, and use the insights gained to improve business operations and performance.
The demand for data science professionals is on the rise, with a projected job growth rate of 36% from 2021 to 2031, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. In a survey by IBM, it was found that businesses that use data and analytics to make decisions are twice as likely to outperform their competitors. This highlights the importance of data science skills in today’s data-driven business environment.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI is transforming various industries, and it has become a crucial skill for IT professionals. AI involves developing computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as speech recognition, image recognition, and decision-making. Knowledge of machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and neural networks is in high demand. AI professionals help businesses develop and implement AI-based solutions that can automate tasks, increase efficiency, and improve overall business performance.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global AI market is expected to reach $407 billion by 2027. This significant growth in the AI market is driving the demand for IT professionals skilled in AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and neural networks. In fact, a report by LinkedIn found that AI specialist roles had a 74% annual growth rate over the last four years.
DevOps:
DevOps is a software development methodology that involves collaboration between development and operations teams to create and deploy software more efficiently. Professionals with skills in DevOps are in high demand, as businesses seek to increase their agility and speed in software development.
According to a report by Zippia, DevOps Engineer was the second most in-demand tech job in the United States in 2020, with a 21% projected job growth from 2018 to 2028.
Blockchain:
Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that can be used to record transactions and store data securely. Professionals with skills in blockchain development, architecture, and security are in high demand, as businesses explore the potential uses of blockchain technology in industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global blockchain market is expected to grow from $7.4 billion in 2022 to $94.0 billion in 2027, at a CAGR of 66.2%. Additionally, a report by Deloitte stated that 24% of US-based executives are currently investing in hiring staff with blockchain experience to support these endeavors, and another 21% are planning to do so within the next calendar year.
User Experience (UX) Design:
UX design involves creating user-friendly and intuitive interfaces for software applications and websites. Professionals with skills in UX design, including user research, interaction design, and usability testing, are in high demand as businesses seek to improve customer satisfaction and engagement.
According to a report by Forrester.com, companies that invest in UX design see a 400% increase in return on investment. Additionally, a survey by UserTesting found that 86% of companies with a dedicated UX budget reported an increase in revenue, and 83% reported an increase in customer satisfaction.
Internet of Things (IoT):
IoT involves connecting devices and objects to the internet to enable them to exchange data and interact with each other. Professionals with skills in IoT development, security, and data analysis are in high demand, as businesses look to leverage the potential of IoT technology in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global IoT market is expected to grow from $300.3 billion in 2021 to $650 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 16.7%. Additionally, a survey by Cisco found that 60% of IoT initiatives fail at the proof-of-concept stage, highlighting the need for skilled professionals to ensure successful implementation.
Project Management:
IT project management involves overseeing the planning, execution, and monitoring of IT projects. Professionals with skills in project management, including agile methodologies, risk management, and stakeholder communication, are in high demand as businesses seek to manage complex IT projects effectively.
According to a report by PMI, 71% of organizations reported using agile approaches to project management in 2020, up from 59% in 2018. Additionally, a survey by VersionOne found that organizations using agile project management saw a 41% increase in productivity and a 37% increase in employee engagement.
Virtual and Augmented Reality:
Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies are increasingly being used in fields such as gaming, education, and healthcare. Professionals with skills in VR/AR development, design, and integration are in high demand, as businesses explore the potential of these technologies to improve user experiences and create new business opportunities.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global VR and AR market is expected to grow from $37 billion in 2022 to $114.5 billion in 2027, at a CAGR of 25.3%. Additionally, a survey by Perkins Coie found that 69% of VR and AR executives expect the technology to become mainstream within the next five years.
Full Stack Development:
Full stack development involves working with both front-end and back-end technologies to create web applications. Professionals with skills in full stack development, including languages like JavaScript, frameworks like React and Angular, and databases like MongoDB and MySQL, are in high demand as businesses seek to develop modern and scalable web applications.
According to Indeed, the average salary for a full stack developer in the United States is $120,749 per year, with job openings for this role growing by 28% year-over-year.
Mobile App Development:
With the widespread use of smartphones and tablets, mobile app development has become a crucial skill for businesses to reach and engage customers. Professionals with skills in mobile app development, including platforms like iOS and Android, programming languages like Swift and Kotlin, and frameworks like React Native and Ionic, are in high demand.
The global mobile application market size is expected to reach $407.31 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 18.4% from 2021 to 2026, according to MarketsandMarkets.
Business Intelligence (BI):
BI involves using data analysis and visualization tools to help businesses make better decisions. Professionals with skills in BI, including data warehousing, data modeling, and data visualization, are in high demand as businesses seek to extract insights from their data to drive growth and innovation.
The global BI and analytics software market is expected to reach $54.27 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 9.1% from 2023 to 2030, according to Fortune Business Insights.
Cloud Architecture:
Cloud architecture involves designing and implementing cloud-based solutions for businesses. Professionals with skills in cloud architecture, including knowledge of platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP, and expertise in areas like cloud security, cloud migration, and serverless computing, are in high demand.
According to a report by Flexera, the use of cloud services increased by 47% in 2020, and 93% of enterprises have a multi-cloud strategy. The report also found that 84% of enterprises have a hybrid cloud strategy.
Robotics Process Automation (RPA):
RPA involves using software robots to automate repetitive tasks and processes. Professionals with skills in RPA, including programming languages like Python and Java, and tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere, are in high demand as businesses seek to increase efficiency and reduce costs through automation.
The global RPA market is expected to reach $8.75 billion by 2024, with an annual growth rate of over 60%, according to Fierce Electronics.
Digital Marketing:
With the growing importance of online marketing channels, digital marketing has become a crucial skill for businesses to reach and engage customers. Professionals with skills in digital marketing, including areas like search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and email marketing, are in high demand.
The global digital advertising market size is expected to reach $786.2 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 15.5%, according to MarketsandMarkets. In the United States, the average salary for a digital marketing manager is $78,155 per year, according to Glassdoor.The global RPA market is expected to reach $8.75 billion by 2024, with an annual growth rate of over 60%, according to Fierce Electronics.
IT Certifications:
There are many certifications available for IT professionals to enhance their skills and demonstrate their expertise to potential employers. Here are some of the popular IT certifications:
CompTIA A+:
The CompTIA A+ certification is an entry-level certification that validates an individual’s understanding of computer hardware, software, and operating systems.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP):
The CISSP certification is a globally recognized certification that validates an individual’s expertise in cybersecurity.
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH):
The CEH certification validates an individual’s skills in identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in computer systems, and it is often sought after by employers in the cybersecurity industry.
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA):
The CCNA certification validates an individual’s skills in networking fundamentals and network security.
CompTIA A+:
This certification validates the skills and knowledge required for entry-level IT support roles such as desktop support technician, help desk technician, and data support technician.
CompTIA Network+:
This certification validates the skills required for a network technician, including configuring, managing, and troubleshooting network devices.
CompTIA Security+:
This certification validates the skills required for a cybersecurity analyst, including risk management, identity management, and security infrastructure.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP):
This certification validates the skills and knowledge required for senior-level cybersecurity roles, including security architecture, security operations, and risk management.
Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA):
This certification validates the skills and knowledge required for auditing, controlling, monitoring, and assessing IT and business systems.
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM):
This certification validates the skills required for managing and overseeing an organization’s information security program.
Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert (MCSE):
This certification validates the skills required for designing, implementing, and administering Microsoft technology solutions.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Certified Solutions Architect:
This certification validates the skills required for designing and deploying scalable, highly available, and fault-tolerant systems on the AWS cloud.
These are just a few examples of IT certifications available. There are many other certifications specific to different technologies, such as Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) for networking, Oracle Certified Professional (OCP) for databases, and Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE) for Linux.
Technical Certifications:
Microsoft Certified Solutions Associate (MCSA): The MCSA certification validates an individual’s skills in designing and deploying Microsoft solutions.
Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA): The RHCSA certification validates an individual’s skills in managing and administering Linux systems.
IT Professional Certifications:
Project Management Professional (PMP): The PMP certification is a globally recognized certification that validates an individual’s skills in project management.
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL): The ITIL certification validates an individual’s knowledge of IT service management.
IT Technical Skills:
Programming: Proficiency in programming languages like Java, Python, and C++ is essential for many IT roles.
Database Management: Knowledge of database management systems like Oracle and SQL Server is critical for IT professionals in roles like database administrator or data analyst.
IT Soft Skills:
Communication: Effective communication is essential for IT professionals to collaborate with team members and communicate complex technical information to non-technical stakeholders.
Problem-Solving: IT professionals must be adept at problem-solving to troubleshoot technical issues and develop innovative solutions to complex problems.
Hiring Strategies

Use a well-defined hiring process
When it comes to hiring for IT positions, it is important for companies to have a well-defined hiring process. This process typically involves a thorough job analysis, development of job descriptions and job postings, sourcing candidates through various channels such as job boards and social media, screening resumes and applications, conducting interviews and reference checks, and making a final job offer.

Use recruiting strategies
In addition to a solid hiring process, companies can also implement various recruiting strategies to attract top IT talent. One effective strategy is to establish a strong employer brand and showcase the company culture and values through social media, company website, and employee testimonials. Another strategy is to offer competitive compensation packages and benefits, including bonuses, stock options, and flexible work arrangements. Companies can also build relationships with IT professionals through networking events, job fairs, and referrals from current employees.

Follow best practices
To ensure successful IT staffing, companies should also follow best practices throughout the hiring process. This includes ensuring that job descriptions accurately reflect the requirements and responsibilities of the position, conducting thorough interviews that assess both technical skills and soft skills such as communication and teamwork, and providing a positive candidate experience throughout the hiring process. Companies should also be transparent about the hiring timeline and communicate regularly with candidates to keep them engaged and informed.

Build a strong employer brand
To attract top IT talent, you need to create a positive image of your company as an employer. This includes focusing on creating a positive company culture, offering competitive salaries and benefits, and showcasing your company's successes and impact. You can build your brand through employee testimonials, highlighting your company's unique value proposition, and promoting your company's involvement in the community.

Leverage social media
Social media platforms such as LinkedIn and Twitter are excellent tools for finding potential candidates and promoting job openings. By creating a strong presence on social media, you can attract candidates who are looking for job opportunities in the IT industry. You can also use social media to highlight your company's culture, showcase employee success stories, and share industry news and trends.

Attend industry events
Attending IT staffing conferences and events is a great way to meet potential candidates and build relationships with other industry professionals. By networking with people in the industry, you can learn about emerging trends and technologies, and identify potential candidates who may be a good fit for your company. You can also use these events to showcase your company's values, culture, and unique selling points.

Offer employee referral programs
Employee referral programs are a great way to leverage your current employees' networks to find potential candidates. Encourage your employees to refer their friends and colleagues to open positions and offer incentives such as bonuses or other rewards to motivate them. This can help you tap into their networks and find candidates who are a good fit culturally and professionally.

Use specialized job boards
Posting job openings on specialized IT job boards can help you reach a targeted audience of job seekers with specific technical skills. These job boards typically have a large pool of qualified candidates and can help you find the right candidate for your open positions quickly. Some examples of specialized IT job boards include Dice, CyberCoders, and Indeed.

Partner with staffing agencies
Partnering with staffing agencies that specialize in IT staffing can be an effective way to find qualified candidates quickly and efficiently. These agencies have access to a large pool of qualified candidates and can help you find the right fit for your company. They also have expertise in the IT industry and can help you identify the right candidate based on your specific needs.

Offer training and development opportunities
Offering training and development opportunities is an effective way to attract candidates who are looking for opportunities to learn and advance their careers. By investing in your employees' growth and development, you can demonstrate that you are committed to their success and show that your company is a great place to work. You can offer training programs, mentorship opportunities, and career development plans to help your employees reach their full potential.
Use a “beyond one-year" approach
You’ll find that most job advertisements appear identical, with companies failing to effectively communicate the value that top candidates can bring to their organization. They often focus solely on the number of years of experience, such as “5 years of experience in X” or “6 years of experience in Y”. Instead, focus on a hiring strategy beyond one-year. The top contenders for any job position usually share several characteristics.
Firstly, they are currently employed and earning a living.
Secondly, they are motivated by factors beyond just a salary increase, such as:

Expanding their skill set and advancing their career prospects

Being presented with challenging technical tasks

Finding their work engaging and stimulating

Having the chance to create an impact and receive acknowledgement for their contributions.

In other words, give the employee a value proposition. Too often the candidate you really want looks at the job ad and just like you assess a resume in 15 seconds or less, they see your job as just another lateral move. Leveraging a beyond year 1 hiring strategy helps the candidate to understand the following:

What opportunities for growth they have.

How they will be technically or mentally challenged in the position.

How the candidate will be able to make a difference in the company.
Ask these questions to yourself

Where do you see the position going?

What would motivate the candidate to choose this position over other competitive offers or their current job?

High-quality candidates who are already employed often view job offers that only offer lateral moves as unappealing. This is especially true in the IT industry, where candidates are typically seeking technical challenges, opportunities for skills growth, access to cutting-edge technology, and recognition, often prioritizing these factors overcompensation. We recommend that you create job advertisements that effectively communicate the opportunities and potential for growth that come with working for your company. By doing so, we attract top-tier candidates who are motivated by the potential for career advancement and personal development. As a result, when we send 2 or 3 candidates to a client, they are often impressed by the quality of the applicants and want to hire 1 or 2 of them. We no longer have to settle for candidates who are scraping the bottom of the barrel.
In your job advertisement, it is important to offer candidates clear guidance on how their performance will be evaluated and the specific factors or metrics that will be used to gauge the success of the position.
Too often, employees have experienced annual reviews in which their manager’s ratings were based on subjective feelings rather than objective data, causing frustration especially when compensation increases are tied to these assessments. Therefore, it is crucial to communicate to candidates that your company has a clear and data-driven approach to performance evaluations, and that there is a defined path they can follow to succeed. By demonstrating your organization’s commitment to objective assessments, you can gain a competitive advantage in attracting top talent.
Outline the following with the candidate:

Performance goals for first 30, 60, 90 Days

Performance goals in Q3 and Q4

Give a little bit of background on what makes the project exciting and the role they would play in making it successful.

Identify the technologies and platforms the candidate will work with.
It Staffing that produce immediate results
What we ask from our clients regarding the position:

Performance Goals


First 30 Days

First 60 Days

First 90 Days

Q3

Q4
Value Proposition

Beyond 1 year, what are the opportunities. Where do you see the position going?

Why would the candidate want to work on this position over the other competing offers, or even their current one?
Project Background


Articulate why the project is exciting.

Define their role to make the project successful.

Convey why the project is challenging.
Technology Stack

Beyond 1 year, what are the opportunities. Where do you see the position going?

Why would the candidate want to work on this position over the other competing offers, or even their current one?
- First 30 Days
- First 60 Days
- First 90 Days
- Q3
- Q4
- Beyond 1 year, what are the opportunities. Where do you see the position going?
- Why would the candidate want to work on this position over the other competing offers, or even their current one?
- Articulate why the project is exciting.
- Define their role to make the project successful.
- Convey why the project is challenging.
- Beyond 1 year, what are the opportunities. Where do you see the position going?
- Why would the candidate want to work on this position over the other competing offers, or even their current one?
Download Whitepaper
Enter the email where we can send the whitepaper.
Talent Acquisition
Talent acquisition is a critical aspect of human resource management that involves finding, attracting, and hiring the best candidates for available job positions. It is a complex process that requires careful planning, effective strategies, and the use of appropriate tools and metrics. The following are some ways to expand on the topic of talent acquisition:

Talent acquisition tools
There are various tools that HR professionals can use to improve their talent acquisition efforts. These tools include applicant tracking systems (ATS), candidate relationship management (CRM) software, talent analytics platforms, and social media recruiting tools. ATS, for example, can help HR teams streamline the recruitment process, manage candidate data, and track the status of job applications. CRM software can help build and maintain relationships with potential candidates, while talent analytics platforms can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of recruitment strategies. Social media recruiting tools, such as LinkedIn and Facebook, can help organizations reach a wider pool of potential candidates and build their employer brand.

Talent acquisition strategies
Developing effective talent acquisition strategies is essential to attract top talent. This can involve creating compelling job descriptions, leveraging employee referrals, using social media to showcase the organization's culture, and partnering with universities and colleges to attract young talent. HR teams can also leverage data to identify the most effective recruiting channels and optimize their recruitment budget.

Talent acquisition metrics
Measuring the effectiveness of talent acquisition efforts is crucial to ensure that the recruitment process is efficient and effective. Key metrics to track include time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, applicant-to-hire ratio, candidate satisfaction, and quality of hire. By monitoring these metrics, HR teams can identify areas for improvement and optimize their recruitment efforts.

Innovative talent acquisition methods
HR teams can explore innovative talent acquisition methods to attract top talent. These can include hosting hackathons, creating immersive virtual experiences, and offering referral bonuses. Additionally, HR teams can consider using artificial intelligence (AI) to automate certain aspects of the recruitment process, such as resume screening and interview scheduling.
Job Postings
Creating effective job postings is crucial in attracting top IT talent. As the competition for skilled IT professionals continues to grow, it is vital for companies to craft job postings that stand out and appeal to the right candidates.
One of the best practices for creating an effective IT job posting is to include clear and concise job descriptions. This means providing detailed information about the job responsibilities, required skills and qualifications, and any relevant experience. Job seekers need to understand exactly what the position entails and what is expected of them.
Highlighting company culture is another key element of an effective IT job posting. Job seekers want to know about the company’s values, mission, and work environment. It is important to showcase what makes your organization unique and attractive to potential candidates.
Using inclusive language is also critical in writing IT job postings. This means avoiding gendered language or other language that could unintentionally exclude certain groups of people. Organizations need to be mindful of using language that promotes diversity and inclusivity, and avoid any language that could create barriers for qualified candidates.
IT job description templates can be a helpful tool for creating consistent and effective job postings. These templates provide a framework for crafting a job posting that includes all the necessary information in a clear and concise format.
In addition to using inclusive language, organizations can also use technology to help remove unconscious bias in job postings. Some software tools can analyze job postings for gendered language or other potentially exclusionary phrases, providing suggestions for more inclusive language.
Overall, crafting effective IT job postings is a critical part of the talent acquisition process. By using best practices such as clear job descriptions, highlighting company culture, and using inclusive language, organizations can attract a diverse pool of top IT talent.

Resume Screening
Effective resume screening is crucial to hiring the best IT talent for your organization. However, with the vast number of resumes that organizations receive for each job posting, it can be a daunting task to sift through them all. That’s why developing effective resume screening techniques is essential.
One of the best ways to start is by creating a list of essential skills and qualifications required for the position. This list can then be used as a guide to screen resumes quickly and efficiently. Another technique is to use applicant tracking systems (ATS) and resume screening tools to help automate the process.
When reviewing resumes, it’s essential to focus on relevant work experience, education, and certifications. Additionally, pay attention to any specific skills or technologies mentioned in the job posting and see if the candidate has experience with them. Keep in mind that candidates with transferable skills and experience in related fields can also be a good fit.
To ensure that the resume screening process is effective and unbiased, it’s important to avoid unconscious bias. This can include making assumptions based on factors such as a candidate’s name, gender, age, or race. Instead, focus on the candidate’s skills and qualifications and try to avoid making assumptions or judgments based on irrelevant factors.
Finally, always be transparent and provide feedback to candidates who apply for the job. Inform them about the status of their application and provide constructive feedback on their resumes if possible. This can help candidates understand where they stand and improve their chances of landing a job in the future.
In summary, effective IT resume screening involves creating a list of essential skills, using ATS and screening tools, focusing on relevant work experience, avoiding unconscious bias, and providing feedback to candidates. By following these tips, organizations can streamline the hiring process and attract the best IT talent to their teams.
Interviewing:
IT interviews are a crucial part of the hiring process, as they allow employers to assess candidates’ technical skills, experience, and cultural fit. To conduct effective IT interviews, hiring managers should prepare a set of relevant and insightful questions that assess the candidate’s qualifications and suitability for the role.
Behavioral IT interview techniques involve asking candidates to provide specific examples of how they have handled various work situations in the past. This technique allows the interviewer to gauge the candidate’s problem-solving skills, communication abilities, and overall work approach.
Technical IT interview techniques involve testing the candidate’s technical skills and knowledge through various methods such as coding challenges, whiteboard exercises, and practical problem-solving scenarios.
It’s important to avoid bias in IT interviews by focusing on the candidate’s qualifications and abilities rather than their age, gender, race, or other personal characteristics. Employers can also use technology to eliminate unconscious bias in the interview process, such as using blind resumes or AI-powered interview tools.
Innovative talent acquisition methods
Prepare thoroughly
Before the interview, review the job description, the candidate’s resume, and any other relevant information. Develop a list of questions that will help you assess the candidate’s qualifications and fit for the role.
Establish rappor
Start the interview by introducing yourself and the company. Create a comfortable and friendly atmosphere for the candidate to help them relax and open up.
Ask open-ended questions
Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple “yes” or “no.” Instead, ask open-ended questions that encourage the candidate to share their experiences, skills, and abilities.
Listen actively
Pay attention to the candidate’s responses and ask follow-up questions to gain a deeper understanding of their qualifications and fit for the role.
Use behavioral interviewing techniques
Behavioral interviewing focuses on how candidates have demonstrated specific competencies in the past. Ask questions that prompt candidates to provide examples of how they have handled situations similar to those they may encounter in the role.
Evaluate cultural fit
Assess the candidate’s values and work style to determine if they will fit well within the company’s culture.
Provide information about the company
Candidates will likely have questions about the company, so be prepared to provide information about the organization’s culture, mission, and values.t information. Develop a list of questions that will help you assess the candidate’s qualifications and fit for the role.
Take notes
Jot down notes during the interview to help you remember key points about the candidate’s qualifications and responses.
Follow up promptly
Let the candidate know when they can expect to hear back from you, and be sure to follow up with them promptly after the interview.
Download Whitepaper
Enter the email where we can send the whitepaper.

Onboarding
IT onboarding is the process of integrating new hires into an organization’s culture and operations. Effective onboarding can help new employees feel welcome, informed, and prepared to succeed in their new roles.
Best practices for IT onboarding include creating a structured and consistent onboarding process, assigning a mentor or buddy to new hires, and providing clear communication and expectations. An IT onboarding checklist can be a helpful tool to ensure that all necessary tasks and information are covered during the onboarding process.
To improve IT onboarding, organizations can also seek feedback from new hires on their onboarding experience and use that feedback to make necessary changes. Employers can also consider using technology to streamline the onboarding process, such as using online training modules or virtual onboarding sessions.
IT Staffing Augmentation Strategies and Best Practices
IT staffing is a crucial aspect of any organization’s success. The right IT professionals can help a company innovate, grow, and achieve its goals. However, finding and hiring the right talent can be a significant challenge. To overcome these challenges, IT staffing augmentation strategies and best practices are essential.
IT Staffing Augmentation Strategies
There are several strategies organizations can use to ensure they have the right IT staff in place. One approach is to create a talent pipeline, which involves building relationships with potential candidates over time. Another strategy is to leverage social media to reach a wider pool of candidates. Referral programs, career fairs, and targeted job postings are also effective strategies for attracting top IT talent.
IT Recruitment Strategies
Recruitment strategies are an essential part of IT staffing. Organizations need to find ways to attract, engage, and retain top IT talent. This can involve creating a strong employer brand, offering competitive compensation and benefits, and providing opportunities for professional development and career advancement.
IT Staffing Best Practices
Effective IT staffing requires a range of best practices. For example, organizations should have clear and concise job descriptions that accurately reflect the skills and experience required for each position. Hiring managers should also use behavioral and technical interview techniques to assess candidates' skills and fit. Furthermore, it's crucial to avoid unconscious bias in all aspects of the hiring process, from resume screening to job interviews.
IT Staffing Challenges
IT staffing challenges can include a shortage of qualified candidates, high demand for certain skills, and competition from other companies. To address these challenges, organizations need to be creative in their approach to IT staffing. For example, they may need to offer more flexibility in work arrangements or consider outsourcing certain IT functions.
IT Staffing Augmentation Trends
IT staffing augmentation is a dynamic field, and there are always new trends and innovations emerging. Some of the most significant trends in IT staffing include remote work, gig economy, and automation. Organizations need to stay up to date with these trends to ensure they are attracting and retaining the best IT talent.
IT Talent Management
Talent management involves ensuring that IT professionals are engaged, motivated, and able to perform at their best. This can involve providing opportunities for training and development, creating a positive work environment, and offering competitive compensation and benefits.
IT Workforce Planning
Effective IT workforce planning involves analyzing an organization's IT staffing needs over time. This can involve identifying skills gaps, forecasting future demand for IT talent, and creating strategies for filling these gaps. Effective workforce planning can help organizations ensure they have the right IT talent in place to meet their business goals. In conclusion, IT staffing augmentation strategies and best practices are essential for any organization that wants to attract and retain top IT talent. By implementing these strategies, organizations can create a strong employer brand, attract a wider pool of candidates, and hire the right IT professionals to help them achieve their business goals.
IT Staffing Roles and Responsibilities
IT staffing is a complex process that involves several roles and responsibilities to ensure successful recruitment and retention of top IT talent. Here are some of the key roles and responsibilities in IT staffing:
IT Staffing Manager
The IT staffing manager is responsible for overseeing the entire IT staffing process. This includes developing and implementing staffing strategies, managing the recruitment team, and ensuring that the staffing process is aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
IT Recruiter
The IT recruiter is responsible for identifying and attracting top IT talent to the organization. They work closely with hiring managers to understand their staffing needs, source candidates, and screen resumes to find the best fit for the position.
IT Talent Acquisition Specialist
The IT talent acquisition specialist is responsible for developing and executing talent acquisition strategies to attract and retain top IT talent. They also work closely with hiring managers to identify staffing needs and develop recruitment plans.
IT HR Manager
The IT HR manager is responsible for overseeing the HR functions within the IT department. This includes managing employee relations, performance management, and staffing activities such as recruitment, onboarding, and retention.
IT Staffing Coordinator
The IT staffing coordinator is responsible for coordinating the logistics of the staffing process, including scheduling interviews, coordinating pre-employment screenings, and managing candidate communication.
IT Staffing Consultant
The IT staffing consultant provides expert advice and guidance on staffing best practices to help organizations meet their IT staffing needs. They may also provide assistance with candidate sourcing, screening, and selection.
IT Staffing Metrics and Analytics
IT staffing metrics and analytics are essential components of managing an effective IT workforce. These metrics and analytics enable organizations to measure the effectiveness of their IT staffing efforts, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their IT talent management strategies.
Some common IT staffing metrics include time to fill, cost per hire, quality of hire, turnover rate, and candidate satisfaction. Time to fill measures the length of time it takes to fill an IT position, while cost per hire measures the total cost of recruiting and hiring a new employee. Quality of hire measures the performance and impact of new hires on the organization, while turnover rate measures the rate at which employees leave the organization. Candidate satisfaction measures the level of satisfaction among job candidates with the hiring process.

IT staffing KPIs (key performance indicators) are specific metrics used to measure the success of IT staffing initiatives. These KPIs can include the number of hires made, the percentage of hires from diverse backgrounds, the time to productivity for new hires, and the retention rate of IT employees.

IT staffing ROI (return on investment) measures the financial impact of IT staffing initiatives on the organization. This metric can help organizations determine the effectiveness of their staffing efforts and make informed decisions about future investments in IT talent management.

IT staffing analytics involves using data analysis techniques to gain insights into IT staffing trends and patterns. This data can be used to identify areas for improvement in IT staffing strategies, evaluate the effectiveness of different recruitment channels, and identify the best sources of IT talent.

IT staffing data analysis involves analyzing large amounts of data to identify trends and patterns in IT staffing. This analysis can help organizations identify areas for improvement in their staffing strategies, evaluate the effectiveness of different recruitment channels, and identify the best sources of IT talent.

IT staffing performance measurement involves evaluating the performance of IT staffing initiatives and making data-driven decisions to improve the effectiveness of these initiatives. By measuring the impact of IT staffing initiatives, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize their IT talent management strategies to achieve better results.
IT Staffing Agencies and Services
IT staffing agencies and services are a valuable resource for companies looking to find top IT talent. These agencies specialize in sourcing, recruiting, and placing IT professionals for a variety of positions, from entry-level to senior-level roles. They have a large network of qualified candidates and can quickly identify potential matches for job openings. Additionally, many IT staffing agencies have experience and expertise in specific industries or areas of IT, such as cybersecurity or software development.
IT staffing augmentation provides a range of HR services related to IT staffing, including recruitment, payroll, and benefits administration. These services can help companies streamline their IT staffing augmentation processes and reduce administrative burdens. IT recruitment agencies and IT headhunters are other types of staffing services that specialize in identifying and recruiting top IT talent for specific roles or industries. They often have a deep understanding of the IT job market and can provide valuable insights into hiring trends and candidate availability.
IT staffing augmentation solutions are customizable staffing options that can be tailored to a company’s specific needs. These solutions can include everything from full-service staffing to targeted recruiting services for specific roles or projects. Both IT staffing augmentation agencies and companies offer a range of services to help organizations find the right talent. They can fill positions on a temporary, contract-to-hire, or permanent basis and provide onsite, offsite, onshore, or nearshore staffing services, depending on their clients’ requirements.
Overall, IT staffing agencies, companies, and services are all available to help organizations fill their IT staffing needs. With a pool of talented IT professionals ready to work, these agencies and services can quickly provide the right talent to clients, saving time and money on recruitment. As such, IT staffing augmentation agencies are becoming increasingly popular, and many organizations are turning to them to handle their staffing needs.
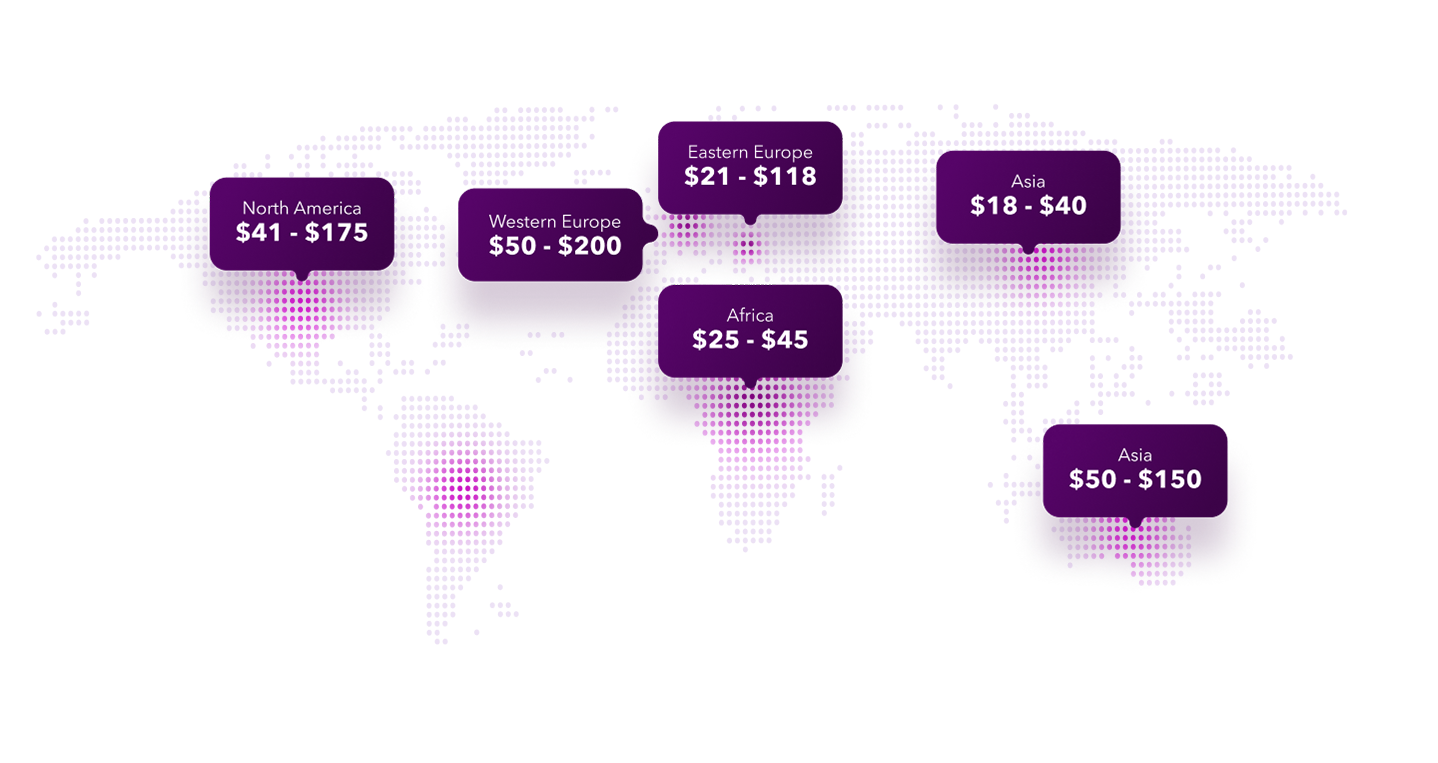
Staffing Augmentation Pricing
Summary
Staffing augmentation is a type of business model where a company hires a third-party provider to provide temporary or contract workers to supplement its in-house staff. This can be a cost-effective way to gain access to specialized skills and expertise without having to commit to hiring full-time employees.
There are several benefits to using staffing augmentation, including:
Reduced costs
Staffing augmentation can help companies save money on hiring and training costs.
Increased flexibility
Staffing augmentation can give companies the flexibility to scale their workforce up or down as needed.
Access to specialized skills
Staffing augmentation can give companies access to specialized skills and expertise that they may not have in-house.
Improved productivity
Staffing augmentation can help companies improve productivity by freeing up their in-house staff to focus on core competencies.
There are a few challenges associated with staffing augmentation, including:
Managing the relationship with the staffing agency
It is important to carefully manage the relationship with the staffing agency to ensure that you are getting the best possible service.
Ensuring that the temporary workers are a good fit for your company culture
It is important to make sure that the temporary workers are a good fit for your company culture and that they are able to work effectively with your in-house staff.
Overseeing the quality of work
It is important to oversee the quality of work that is being done by the temporary workers to ensure that it meets your standards.
Overall, staffing augmentation can be a valuable tool for businesses that are looking to improve their efficiency and productivity. However, it is important to carefully consider the benefits and challenges before making a decision to use staffing augmentation.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind when considering staffing augmentation:
The type of staffing augmentation that you need will depend on your specific business needs. There are a variety of staffing models available, so it is important to choose one that is right for you.
When choosing a staffing agency, it is important to do your research and make sure that you choose a reputable agency with a good track record.
It is important to set clear expectations with the staffing agency and to communicate regularly with them to ensure that you are getting the service that you need.
It is important to provide the temporary workers with the training and support that they need to be successful.
It is important to evaluate the performance of the temporary workers on a regular basis and to make sure that they are meeting your expectations.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your staffing augmentation experience is a success.